SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificates are digital credentials that secure the connection between your web browser and a website. These certificates secure the connection between your browser and a website by encrypting data like passwords and verifying the site’s legitimacy. This protects your information from attackers and prevents fake sites. A padlock icon in the browser shows when a site uses these certificates.
The CA/B Forum has officially approved a phased reduction of public SSL/TLS certificate lifespans, resulting in a 47-day maximum validity by March 2029. Backed by Apple, Google, Mozilla, and Microsoft, this change also reduces domain validation reuse to 10 days. Domain Control Validation (DCV) is the process used by Certificate Authorities (CAs) to verify that someone requesting an SSL/TLS certificate actually owns or controls the domain in question. This change is designed to enhance security but brings new operational challenges for organizations.
Timeline of SSL/TLS Certificate Validity Reductions
The validity period of SSL/TLS certificates has steadily decreased over the years to strengthen online security. This shift reflects the growing need for quicker key rotation, faster response to vulnerabilities, and improved cryptographic practices. Below is a timeline showing how these changes evolved and why they were necessary.
2011: Certificates Valid for 8-10 Years
- Why so long?
Early on, CAs and browser vendors allowed long validity periods because the web’s security infrastructure was less mature. The focus was on convenience, minimizing administrative overhead for organizations and users. Long lifespans meant fewer renewals, making certificate management easier but at the cost of security agility.
- Drawbacks:
Long-lived certificates meant vulnerabilities (like compromised keys or outdated cryptographic algorithms) remained in use for years, increasing security risks.
2015: Reduced to 3 Years
- Reason for Reduction:
By 2015, the industry recognized the need for more frequent key rotation to improve security. Cryptographic standards were evolving rapidly, and long-lived certificates were seen as risky because they prolonged exposure to potential compromises.
- Impact:
The reduction encouraged organizations to renew certificates more often, facilitating better security hygiene, but still kept renewals manageable.
2018: Reduced to 2 Years
- Why Further Shorten?
With rising cyber threats and faster advances in cryptanalysis, a 3-year window was deemed too long to adequately respond to emerging vulnerabilities. Shortening to 2 years aligned better with best practices in cryptographic lifecycle management.
- Industry Push:
Browser vendors and the CA/Browser Forum pushed for this change to enhance web security and reduce the risk of misuse or compromise.
September 2020: Reduced to 398 Days (about 13 Months)
- Motivation:
The shift to roughly 1-year validity reflected the need for agile response to threats, faster key rotations, and quicker adoption of updated cryptographic standards. This change made it harder for attackers to exploit compromised certificates for extended periods.
- Browser enforcement:
Major browsers enforced this limit to improve overall internet security, requiring more automation in certificate management.
Current (2025): Still 398 Days
- Upcoming Changes:
The CA/Browser Forum has approved a phased reduction to a 47-day maximum lifespan by March 2029, with domain validation reuse cut to 10 days.
- Why Now?
The faster turnover aims to drastically reduce risks associated with compromised certificates, misissuance, and outdated cryptography. It also supports the evolving landscape of security standards, including quantum-resistant algorithms.
- Operational Challenges:
This will require organizations to adopt highly automated and scalable certificate management systems to handle frequent renewals and validations without errors.
What Is Changing?
The CA/Browser Forum has approved a phased reduction in certificate lifespans. This means certificates must be renewed much more frequently, making manual processes unsustainable for most organizations.
| Date | Maximum Validity Period | DCV Reuse Period |
|---|---|---|
| March 15, 2026 | 200 days | – |
| March 15, 2027 | 100 days | – |
| March 15, 2029 | 47 days | 10 days |
In 2023, Google proposed reducing TLS certificate lifespans from 398 days to just 90 days to enhance security and encourage automation. Apple went a step further, recommending a 47-day limit. After industry discussions, the CA/Browser Forum approved a phased plan to adopt 47-day certificates by 2029. Major browsers have backed this move to lower risks and ensure safer web connections.
Organizations still running older, deprecated TLS versions, such as TLS 1.0 or TLS 1.1, or relying on weak cipher suites like RC4 or SHA-1, face serious security and operational challenges. These outdated protocols and algorithms are vulnerable to attacks like POODLE and BEAST, and modern browsers and CAs no longer support them.
With the shift to shorter certificate lifespans and stricter security policies, organizations must upgrade their systems to at least TLS 1.2 or preferably TLS 1.3. They should also replace weak ciphers with stronger options like AES-GCM and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). This is because these modern algorithms offer better performance and higher security. AES-GCM provides authenticated encryption, which helps prevent data tampering, while ECC offers strong encryption with shorter key lengths, making it faster and more efficient.
The Pros
Using shorter certificate lifespans is a simple way for organizations to improve their security. When certificates are replaced more often, it’s harder for attackers to take advantage of any that are compromised. This approach helps limit the damage from potential security threats and makes it easier to keep systems safe and up to date. Shorter certificate lifespans offer clear security benefits like the following:
- Reduced Attack Surface: Compromised certificates are valid for a shorter time, limiting the risk involved, such as data breaches. By minimizing the time a compromised certificate can be exploited, organizations reduce the risk of prolonged security incidents, regulatory penalties, reputational harm, and financial losses caused by downtime or breaches. In high-stakes environments, this shorter exposure time can significantly lower both security and business impact.
Example – SSL.com Certificate Misissuance (April 2025): In April 2025, SSL.com discovered a flaw in its DCV process that allowed users to improperly validate domains they didn’t own. This led to the misissuance of 11 SSL/TLS certificates, which could have been exploited to host spoofed websites or carry out man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. Although the certificates were revoked within 24 hours of discovery, the incident highlighted the danger of relying on long-lived certificates when validation errors occur. - Up-to-Date Security: Automated certificate renewals help organizations keep up with modern cryptographic standards like SHA-2, RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman), ECC, and many more. They reduce the risk of using outdated or weak algorithms by ensuring regular updates. As certificate lifespans get shorter, renewals become more frequent, thus creating natural points to evaluate cryptographic strength, rotate keys, and phase out old encryption methods.
This approach not only strengthens current security but also makes it easier to adopt new standards like post-quantum cryptography when the time comes. Without automation, maintaining this level of cryptographic routine and scaling it is nearly impossible. Mozilla and Google’s decision to distrust Entrust in 2024 highlights the need for agility in certificate management. With 47-day lifespans, organizations can switch CAs faster, reduce reliance on long-term trust anchors, and respond quickly to compliance issues.
- Simplified Certificate Inventory Management: Frequent renewals encourage better certificate tracking and awareness. Organizations gain real-time visibility into which certificates are active, reducing “forgotten” or orphaned certificates that can cause security gaps. In 2023, Cisco reported that frequent certificate renewals helped them identify and remove orphaned certificates across their network, improving security and preventing unexpected outages.
- Supports Zero-Trust Security: By continuously validating certificates, organizations avoid trusting expired or revoked certificates, keeping access tightly controlled. However, manual certificate management makes this difficult, leaving room for human error and delayed responses. Our certificate lifecycle management (CLM) solution, CertSecure Manager, will help you automate the entire certificate lifecycle, reducing risk, saving time, and keeping your organization aligned with security goals.
- Better Compatibility with Cloud and DevOps: Modern cloud-native environments and automated pipelines benefit from frequent certificate rotations, improving integration with ephemeral infrastructure and minimizing stale credentials.
The Cons
- Exponential Workload Increase: Moving from 398 days to 90 or even 47 days means up to four times as many renewals annually. For a company managing hundreds or thousands of certificates, this quickly becomes overwhelming. For example, an e-commerce business with 500 certificates would need to process over 2,000 renewals annually, significantly increasing the administrative burden.
- Manual Management Becomes Impractical: Tracking, renewing, and deploying certificates manually is error-prone, leading to outages, compliance failures, and security lapses. For instance, Microsoft Teams suffered a three-hour outage in 2019 when an expired authentication certificate left 20 million users unable to access the platform. The incident highlighted the risks of manual certificate management, even for major tech companies.
If Microsoft had implemented shorter-lived certificates, such as a 47-day validity period combined with automated renewal and monitoring, the expired certificate would likely have been detected and replaced well in advance. Shorter validity enforces more frequent checks and reduces the window for certificate-related failures, making outages like this far less likely. This case underscores the importance of enforcing tighter renewal cycles and automation in CLM.
- Resource Strain: IT teams must dedicate more time, staff, and training to certificate management, diverting focus from strategic work. In smaller organizations, the increased workload may force teams to delay critical upgrades or security improvements.
- Risk of Outages: Expired certificates cause service disruptions, loss of customer trust, and potential revenue loss. According to the 2022 State of Machine Identity Management Report, around 81% of organizations report certificate-related outages each year. For example, Google Voice experienced a global outage in 2021 due to an expired TLS certificate, leaving users unable to make calls for hours. Similarly, Cisco’s SD-WAN devices faced failures when a hardware certificate expired, affecting enterprise connectivity and requiring urgent intervention.
- Compliance Complexity: Maintaining evolving standards and audit requirements becomes more challenging without automation. In the Equifax breach, a monitoring device’s certificate expired and went unnoticed for 19 months, allowing attackers to access sensitive data undetected. At the time, Equifax had 324 expired SSL certificates, including 79 on critical monitoring devices, demonstrating how lapses in certificate management can lead to severe compliance failures and regulatory penalties.
Automation: The Only Viable Solution
With certificates requiring more frequent renewals, manual management is no longer practical, as it increases the risk of human error, missed deadlines, and potential service disruptions. According to the CA/Browser Forum, which governs certificate standards, shorter certificate lifespans are part of a broader strategy to enhance security and adaptability to emerging cryptographic standards.
Organizations managing large-scale certificate inventories must adopt automated systems to handle renewals across multiple platforms, ensuring scalability. However, automation also presents challenges:
- Automating Certificate Revocation: Revoking certificates in real-time and ensuring all dependent systems reflect the change can be difficult.
- Timely Propagation: Revocation status must be distributed quickly via OCSP and CRLs to avoid stale or vulnerable certificates remaining trusted.
- OCSP Stapling and CRL Management: These require careful configuration to ensure browsers and systems receive up-to-date revocation information.
- Dependency Management: Certificates often have application or service dependencies that need coordination during updates or revocation.
- Audit & Visibility: Ensuring automated actions are logged and traceable is important for adhering to compliance requirements and troubleshooting.
- Downtime Risk: Improper automation can cause unexpected service outages.
Automation streamlines the renewal process and helps maintain compliance with security policies and regulatory standards, which is essential in preventing security vulnerabilities. Furthermore, automating certificate management can significantly reduce the risks of errors, downtime, and potential security breaches, thus improving cost-efficiency and operational reliability. As the need for quicker security increases, automation has become essential for businesses to stay secure and compliant.
Recommended Steps to Implement Automation
Organizations are expected to meet security standards, follow compliance rules, and keep services running smoothly. As digital systems grow and certificate use increases, it is important to follow industry recommendations. These are based on real challenges and help reduce risks like expired certificates or security issues. By using these guidelines, teams can improve security, avoid manual errors, and stay prepared for audits and policy changes.
- Conduct a complete audit of your certificate inventory
- Identify platforms and systems requiring automation
- Select a comprehensive CLM solution
- Integrate the CLM with existing infrastructure and DevOps pipelines
- Define renewal, issuance, and revocation policies
- Schedule regular compliance checks and reporting
Encryption Consulting’s CertSecure Manager
CertSecure Manager by Encryption Consulting LLC is built to tackle the challenges of shifting to shorter certificate lifespans, like 47 days. With these changes, automation becomes essential for efficiently managing the new certificate environment.
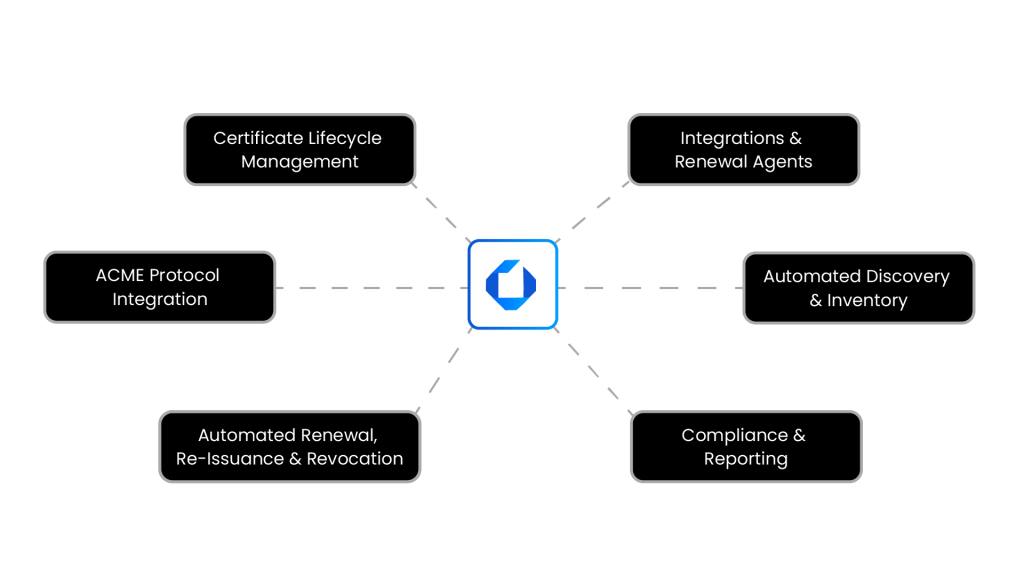
1. Implement a CLM Solution
A CLM solution is key to efficiently handling internal and external certificates, ensuring cryptographic compliance, and streamlining certificate inventory and reporting. CertSecure Manager, for example, provides a comprehensive solution that automates the entire certificate lifecycle from discovery to deployment, renewal, and revocation, minimizing the manual effort involved in managing certificates.
It also automates compliance checks to ensure all certificates meet industry standards like PCI-DSS, GDPR, and ISO. Comprehensive reports are generated for audits, simplifying compliance processes.
2. Automated Certificate Discovery and Inventory
CertSecure Manager automatically discovers all certificates across your infrastructure, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments. It provides a complete certificate inventory, ensuring no certificate is left unmanaged, including self-signed certificates that may pose a security risk. With this centralized inventory, you can quickly identify certificates due for renewal, significantly reducing the risk of expired certificates causing issues.
3. Advanced ACME Protocol Integration
By leveraging the ACME protocol, CertSecure Manager automates the issuance and renewal of certificates in a secure, standardized manner. This eliminates manual intervention, ensuring certificates are always renewed on time, even with the frequent renewal cycles required by shorter validity periods like 47 days.
4. Automated Renewal, Re-Issuance, and Revocation
CertSecure Manager automates certificate renewal and reissuance, ensuring certificates are always up to date. It also revokes compromised or unnecessary certificates, reducing security risks and ensuring compliance.
This automation ensures uninterrupted operations within an organization and enhances security by quickly addressing compromised or unnecessary certificates. It makes meeting compliance requirements easier by managing certificates on time, keeping clear records, and improving security, while reducing workload and building trust.
5. Compliance and Reporting
CertSecure Manager automates compliance checks, ensuring your certificates meet industry standards like NIST, HIPAA, and GDPR. It generates comprehensive reports for audit purposes, making it easier to comply with regulatory requirements. These reports also help you assess your certificate infrastructure and identify potential weaknesses before they become problematic.
6. Seamless Integrations and Renewal Agents for Enhanced Certificate Management
CertSecure Manager integrates with various tools and platforms, including Terraform, Ansible, Azure Key Vault, and Splunk, to ensure streamlined certificate management. It automates certificate provisioning, renewal, and deployment within CI/CD pipelines across databases, web servers (Apache, IIS, NGINX), and more. Renewal agents are customized for these services, ensuring that certificates are consistently updated and secure.
As the industry is now shifting to 47-day certificate validity periods, CertSecure Manager’s integrations and automated processes help maintain security, compliance, and uptime by handling renewals and managing certificates across diverse environments with minimal manual effort.
Conclusion
The move to 47-day TLS certificate validity is just one example of how digital security is evolving to meet modern threats. While shorter certificate lifespans greatly reduce the risk of compromise, they also demand more advanced and automated management processes. To stay ahead, organizations need comprehensive solutions that automate certificate lifecycles and address broader security and compliance needs.
Encryption Consulting offers a full range of security services and certificate management, including PKI audits, enterprise PKI design and optimization, encryption audits, and code signing solutions through our CodeSign Secure platform. We support Zero Trust and provide ongoing compliance advice and help secure digital assets with strong identity and encryption practices. Our expertise ensures your organization stays protected, compliant, and prepared for evolving cybersecurity challenges.