- What Is SIEM and Why Does It Matter for Modern Enterprises?
- Why Is SIEM Important in Modern Security Architecture?
- How Does SIEM Work?
- Introducing Splunk: A Modern and Scalable SIEM
- How Splunk Works: From Raw Data to Real Insights
- Integrating CertSecure Manager with Splunk via HTTP Event Collector (HEC)
- Why Does CertSecure Manager Need SIEM Integration?
- What Is HTTP Event Collector (HEC), and Why Did We Choose It?
- Step-by-Step Integration of CertSecure Manager with Splunk
- Why This Integration Is Crucial: Key Benefits
- Conclusion
What Is SIEM and Why Does It Matter for Modern Enterprises?
Modern enterprise infrastructure is a sprawling ecosystem comprising clouds, endpoints, applications, servers, and APIs, all constantly generating logs. These logs carry vital signals about system health, security posture, and operational behavior. However, when these logs exist in isolation, scattered across different systems and formats, they’re just fragmented data points. Without correlation or context, they offer little actionable insight. It’s only when logs are centralized, normalized, and analyzed together that they reveal meaningful patterns, highlight risks, and drive informed decisions. In other words, raw logs are meaningless, but unified visibility turns that into intelligence data.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solves this by acting as a centralized intelligence layer. It collects, parses, analyzes, and correlates logs from across your environment, giving security teams full visibility and the power to act fast.
At its core, SIEM combines two previously separate disciplines:
- Security Information Management (SIM): Focused on the long-term storage, analysis, and reporting of log data.
- Security Event Management (SEM): Concentrates on real-time monitoring, correlation, and incident response.
By merging these capabilities, SIEM acts as a command center for security operations, enabling both historical analysis and real-time threat detection.
Why Is SIEM Important in Modern Security Architecture?
Enterprises today face an overwhelming volume of logs and alerts, many of which could signal malicious activity. On average, a Security Operations Center (SOC) may receive over 10,000 alerts per day, and large organizations may see well over 150,000. Amid this deluge, manually identifying meaningful threats is nearly impossible without automation and intelligence.
A well-implemented SIEM gives real-time visibility across on-prem, cloud, and hybrid assets, allowing analysts to detect anomalies, trace malicious activity, and respond before incidents escalate. It helps reduce false positives by intelligently filtering out noise, ensuring teams focus only on genuine threats.
Ultimately, SIEM helps prevent costly breaches, supports compliance, and enables security teams to work smarter, not harder, in the face of relentless cyber risks.
How Does SIEM Work?
SIEM works by collecting, analyzing, and correlating log and event data from various sources such as servers, operating systems, firewalls, antivirus tools, and enterprise applications, and centralizing that information for security monitoring and threat detection.
Once data is ingested, the SIEM platform categorizes it into meaningful events such as login attempts, malware detection, or privilege escalations. Based on defined rules and behavioral baselines, it then triggers alerts for any suspicious or anomalous activity.
For instance, a user failing to log in 10 times in 15 minutes might generate a low-priority alert. However, 500 failed attempts in the same window would immediately trigger a high-priority alert, indicating a possible brute-force attack.
Introducing Splunk: A Modern and Scalable SIEM
Splunk is one of the most widely adopted enterprise SIEM platforms. It handles massive volumes of data, supports real-time analytics, and is built for flexibility.
To truly understand Splunk, it helps to think beyond traditional application models. Splunk is not a single-purpose tool; it’s a data platform. It doesn’t serve just one fixed function, like creating logs or visualization. Instead, Splunk is more like a toolbox for machine data, giving you the ability to collect, search, correlate, analyze, and visualize vast amounts of real-time and historical data generated by your systems.
How Splunk Works: From Raw Data to Real Insights
Splunk is more than just software; it’s an end-to-end data platform designed to help organizations make sense of the overwhelming amount of data their digital environments generate. But how exactly does it accomplish this? Let’s walk through Splunk’s key operations in detail, from data ingestion to actionable insights.
Step 1: Collecting and Ingesting Data
At the core, Splunk collects data from virtually any source within a company’s digital environment. This includes structured and unstructured logs, metrics, and traces coming from servers, applications, networks, and security devices. Whether you’re managing a small set of servers or thousands of endpoints across global data centers, Splunk can ingest data seamlessly.
Splunk doesn’t restrict you to a specific type of input; it’s highly flexible. One can ingest data using traditional methods like Syslog (for network and firewall logs), dedicated Splunk forwarders installed on servers, or through REST APIs and cloud integrations. One of Splunk’s most powerful ingestion methods is its HTTP Event Collector (HEC), a simple yet secure way to send JSON-formatted data directly into Splunk without needing additional agents or infrastructure.
Step 2: Indexing and Storing Data
Once the data reaches Splunk, it doesn’t just sit idle. Splunk indexes this incoming data, processing and organizing it in a way that makes searches lightning-fast, even across vast amounts of data. This structured indexing allows Splunk to handle queries rapidly.
Step 3: Analyzing, Correlating, and Visualizing Data
This step is where Splunk truly becomes invaluable. Once your data is indexed, Splunk provides powerful search and analytical capabilities using its proprietary language, Search Processing Language (SPL). SPL is intuitive yet powerful, allowing you to ask complex questions and receive instant answers.
This cohesive workflow, from raw data ingestion to actionable intelligence, is why Splunk is trusted by organizations worldwide as the central nervous system of their digital infrastructure.
Integrating CertSecure Manager with Splunk via HTTP Event Collector (HEC)
When managing certificates at scale, visibility isn’t optional; it’s essential. Certificate-related incidents, such as expired or unauthorized access to certificates, can cause significant downtime or security breaches. To proactively manage this risk, we integrated CertSecure Manager directly with Splunk using its powerful HTTP Event Collector (HEC). This allowed us to centralize, analyze, and monitor certificate lifecycle events in real-time.
Why Does CertSecure Manager Need SIEM Integration?
CertSecure Manager automates certificate lifecycle management (CLM) for enterprises, handling critical operations like certificate issuance, renewal, revocation, and expiry tracking. Each of these events generates essential logs, but isolated logs aren’t useful unless they are centralized, correlated, and actionable.
By sending CertSecure Manager’s certificate lifecycle events directly to Splunk, we achieved several vital capabilities:
- Real-time certificate monitoring: Real-time monitoring of certificates ensures instant visibility into key events like expirations, revocations, or unauthorized issuances. Instead of relying on manual checks or periodic audits, Splunk provides immediate alerts. This helps prevent service disruptions due to expired certificates and mitigates potential breaches from compromised ones.
- Enhanced visibility and correlation: Correlate certificate events with broader security data (like firewall logs, user access, or unusual behaviors). By linking certificate revocations to suspicious login attempts or anomalous network activity, Splunk quickly surfaces hidden threats.
- Audit and compliance readiness: With Splunk’s centralized logging, compliance and audit processes become streamlined and accurate. All certificate-related events, issuances, revocations, and renewals are securely logged, timestamped, and easily searchable. This capability dramatically simplifies audits for standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 by providing ready-made reports and proof of compliance.
What Is HTTP Event Collector (HEC), and Why Did We Choose It?
Splunk’s HTTP Event Collector (HEC) is a REST-based API designed specifically for high-performance, secure, and reliable log ingestion directly over HTTPS. HEC allows external applications, such as CertSecure Manager, to send structured JSON log data into Splunk easily and securely, without the need for additional agents or log-forwarding software. The agentless design removes the need for additional log forwarders or complex configurations, making the integration process simpler and lightweight.
Lastly, its capability to ingest logs in real-time meant that certificate events became instantly searchable and visualizable within Splunk, significantly improving our ability to monitor and respond to certificate-related incidents proactively.
Step-by-Step Integration of CertSecure Manager with Splunk
Here’s how we set up the CertSecure Manager for Splunk integration in detail:
1. Configuring Splunk HEC
First, in Splunk, we must configure the HTTP Event Collector:
- Navigate to: Settings → Data Inputs → HTTP Event Collector → New Token.
- Name the token: CertSecure_HEC.
- Enable indexing acknowledgment to ensure logs are reliably ingested.
- Assign logs to a dedicated index named certsecure_index.
- Set the sourcetype as certsecure_clm for querying.
Splunk then provides us with a secure HEC Token (a unique authentication key) and an endpoint URL like:
https://splunk.mycompany.com:8088/services/collector/event
2. Configuring CertSecure Manager
On the CertSecure Manager side, we configure our logging and event module to send JSON-formatted logs directly to Splunk’s HEC endpoint. The configuration involves the following steps:
-
Adding the HEC endpoint and token into CertSecure Manager’s configuration file:
HEC_ENDPOINT=splunk.mycompany.com
HEC_TOKEN=your-splunk-generated-token
Port=8088 (default)
Protocol: https or http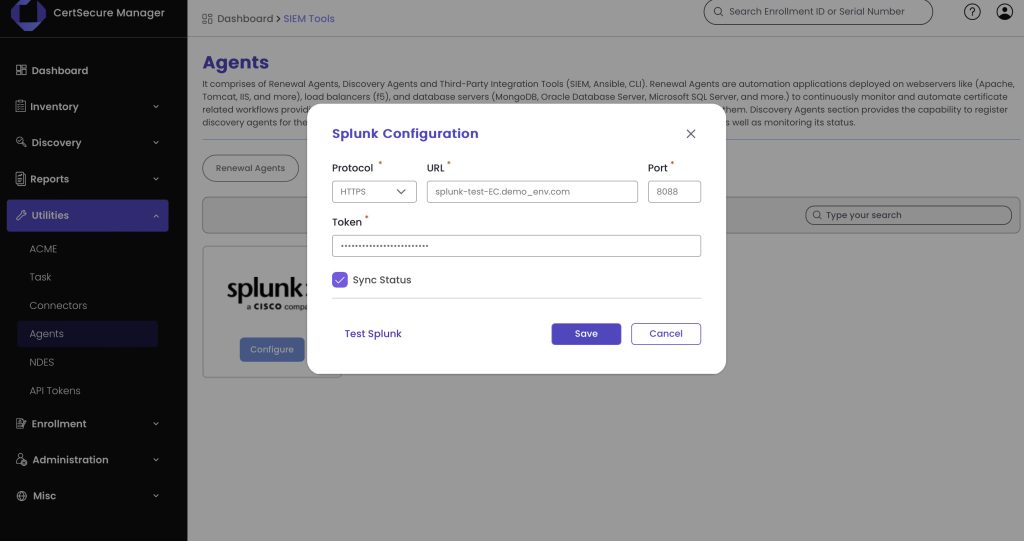
- Now, we can go ahead and test a sample ingestion.
3. Verifying Data Ingestion in Splunk
To verify successful data ingestion, we can immediately test log delivery with Splunk’s Search interface using:
index=certsecure_index, sourcetype=certsecure_clm
This instantly shows real-time certificate events flowing into Splunk, confirming successful integration.
Why This Integration Is Crucial: Key Benefits
Integrating CertSecure Manager with Splunk through the HTTP Event Collector (HEC), is essential for organizations aiming to strengthen their cybersecurity posture, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain compliance. The integration provides several strategic advantages, transforming certificate management from a manual, error-prone task into proactive, automated intelligence.
Deep Visibility and Correlation
One of the most powerful advantages of the integration is its ability to correlate certificate lifecycle events with broader security data. Splunk doesn’t just store logs; it intelligently connects data points, such as certificate revocations with unusual login patterns, firewall alerts, or suspicious network traffic. By providing this comprehensive contextual view, organizations can uncover hidden threats and subtle anomalies that isolated monitoring might miss, allowing for proactive threat hunting and a significantly improved security posture.
Real-Time Alerting
Through real-time alerting, Splunk continuously monitors certificate-related events such as impending expirations or immediate revocations. It instantly triggers alerts whenever it detects critical certificate issues, enabling organizations to intervene swiftly before these issues become operational disruptions or security threats.
Improved Incident Response
The integration significantly enhances incident response capabilities by rapidly surfacing suspicious activities around certificates. With Splunk analyzing real-time data from CertSecure Manager, anomalies such as unexpected certificate issuance or unauthorized access attempts can be immediately identified. This helps security teams to investigate and remediate potential threats swiftly and minimize damage from incidents.
Resource Efficiency
Finally, the integration reduces administrative overhead by removing manual, spreadsheet-based certificate tracking and reporting. By automating real-time monitoring and reporting processes, the CertSecure Manager-Splunk integration frees up valuable IT and security resources to focus on strategic tasks rather than routine management. This automation not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces human errors.
Conclusion
The integration of CertSecure Manager with Splunk via the HTTP Event Collector (HEC) has transformed our approach to certificate lifecycle management. What once was a fragmented, reactive process, tracking events manually, responding after problems surfaced, is now centralized, automated, and proactive.
By leveraging the powerful combination of CertSecure Manager’s automated certificate handling and Splunk’s advanced SIEM capabilities, organizations gain unmatched visibility into their certificate landscape. This integration enables real-time alerts, rapid incident response, deeper security correlations, and significant resource savings.
In conclusion, the CertSecure Manager and Splunk integration not only enhances operational efficiency but also transforms certificate lifecycle management into a strategic component of your cybersecurity posture, equipping your organization to anticipate, detect, and respond swiftly to emerging threats and challenges.
- What Is SIEM and Why Does It Matter for Modern Enterprises?
- Why Is SIEM Important in Modern Security Architecture?
- How Does SIEM Work?
- Introducing Splunk: A Modern and Scalable SIEM
- How Splunk Works: From Raw Data to Real Insights
- Integrating CertSecure Manager with Splunk via HTTP Event Collector (HEC)
- Why Does CertSecure Manager Need SIEM Integration?
- What Is HTTP Event Collector (HEC), and Why Did We Choose It?
- Step-by-Step Integration of CertSecure Manager with Splunk
- Why This Integration Is Crucial: Key Benefits
- Conclusion




