In this article, we will take a closer look at Google’s Cloud Key Management Services. When users store data into Google Cloud, the data is automatically encrypted at rest. We use Google’s Cloud Key Management service to gain better control over managing the encrypted data-at-rest and encryption keys.
Source and Control of cryptographic keys
Cloud KMS lets users manage cryptographic keys in a central cloud service for direct use or use with other resources and applications. The keys that have to be used must be from one of these sources:
- Cloud KMS’s software backed key gives users the ability to encrypt data with either a symmetric or asymmetric key that the users control.
- Cloud HSM provides hardware keys. Symmetric and asymmetric keys are only used in FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated Hardware Security Modules (HSMs).
- Bring Your Own Key(BYOK) is also available for users to import their cryptographic keys into Cloud KMS.
- Cloud External Key Manager (Cloud EKM), which uses external Key Managers such as Thales or Fortanix can also be used.
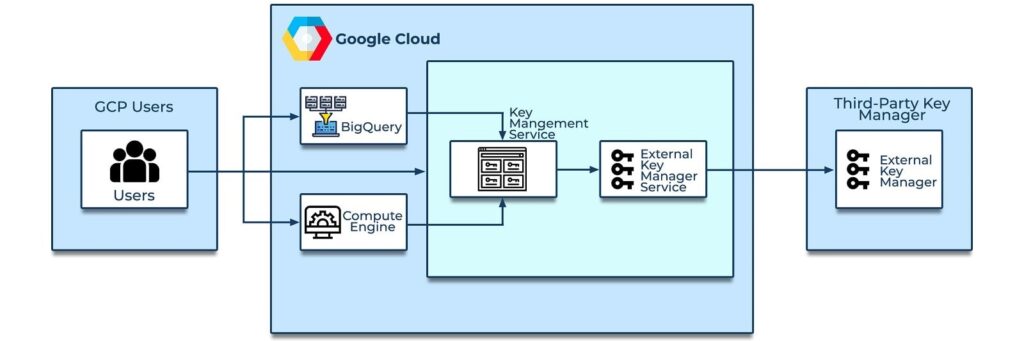
Figure: Cloud EKM providing bridge between KMS and External Key Manager
Cryptographic keys in Cloud KMS
This section describes keys, key versions, and the grouping of keys into keyrings. The following diagram illustrates key groupings.
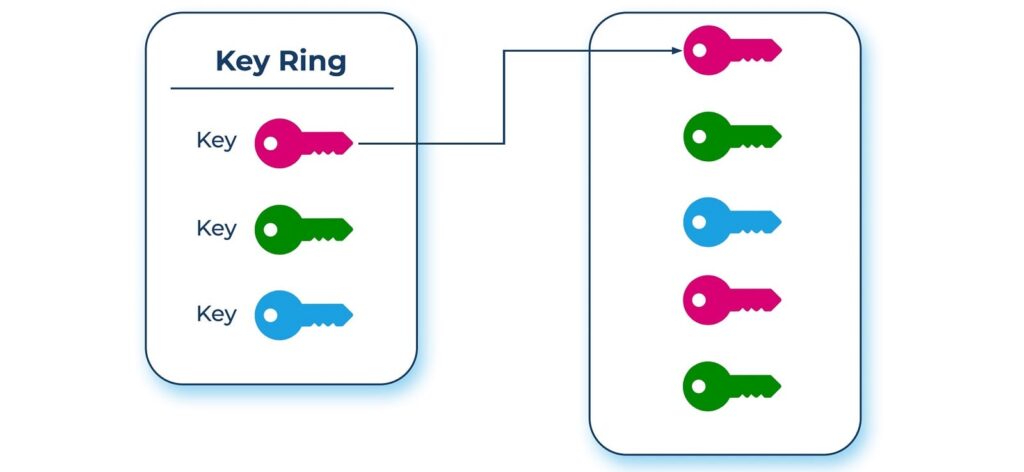
Key: A named object which represents a cryptographic key. It is a pointer to a key, and the actual bits or the key may change as we rotate the keys or create newer versions of the keys.
Cloud KMS supports both asymmetric keys and symmetric keys. A symmetric key is used for symmetric encryption to protect some corpus of data, such as using AES-256 in GCM mode to encrypt a block of plaintext. An asymmetric key can be used for asymmetric encryption or for creating digital signatures.
Cloud KMS components
In this section, we discuss a few points about additional parameters associated to Google CloudKMS resources such as keys and keyrings.
- Project Google Cloud KMS resources belong to Google Cloud Project, like all other Google Cloud Resources. Users can host data in a project that is different from the project in which Cloud KMS keys reside. This capability supports the best practice of separation of duties between the key administrators and data administrators.
- LocationsWithin a project, Cloud KMS resources are created in one location.
Key Hierarchy
The following diagram illustrates the key hierarchy of Google’s internal Key Management Service. Cloud KMS leverages Google’s internal KMS in that Cloud KMS-encrypted keys are wrapped by Google KMS. Cloud KMS uses the same root of trust as Google KMS.

- Data encryption key (DEK): A key used to encrypt data.
- Key encryption key (KEK): A key used to encrypt, or wrap, a data encryption key. All Cloud KMS platform options (software, hardware, and external backends) let you control the key encryption key.
- KMS Master Key: The key used to encrypt the key encryption keys (KEK). This key is distributed in memory. The KMS Master Key is backed up on hardware devices. This key is responsible for encrypting your keys.
- Root KMS: Google’s internal key management service.
Cloud KMS platform overview
The Cloud KMS platform supports multiple cryptographic algorithms and provides methods to encrypt and digitally sign using both hardware and software-backed keys.
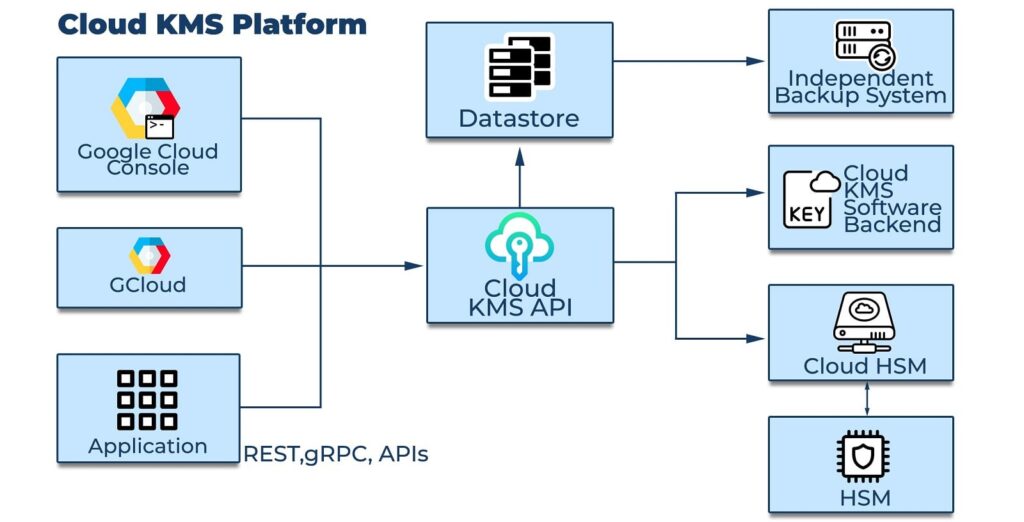
The diagram shows the main components of the Cloud KMS platform.Administrators access key management services by using the Google Cloud Console, the gcloud command-line tool, or through applications implementing the REST or gRPC APIs.Applications access key management services using a REST API or gRPC.
Applications can use Google services that are enabled to use customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK). CMEK, in turn, uses the Cloud KMS API. The Cloud KMS API lets users use either software (Cloud KMS) or hardware (Cloud HSM) keys. Both software and hardware-based keys leverage Google’s redundant backup protections.
With the Cloud KMS platform, users can choose a protection level when creating a key to determine which key backend creates the key and performs all future cryptographic operations on that key.
The Cloud KMS platform provides two backends (excluding Cloud EKM), which are exposed in the Cloud KMS API as
- Software Protection Level The protection level software applies to keys that may be unwrapped by a software security module to perform cryptographic operations.
- HSM protection Level The protection level HSM applies to keys that can only be unwrapped by Hardware Security Modules that perform all cryptographic operations with the keys.
Google Cloud supports CMEK for several services, including
- Cloud Storage
- BigQuery
- Compute Engine.
CMEK lets users use the Cloud KMS platform to manage the encryption keys that these services use to help protect their data.Cloud KMS cryptographic operations are performed by FIPS 140-2 validated modules.
- Keys with protection level software, and the cryptographic operations performed with them, comply with FIPS 140-2 Level 1.
- Keys with protection level HSM, and the cryptographic operations performed with them, comply with FIPS 140-2 Level 3.
References
www.cloud.google.com/security-key-management