Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) allows software on routers and other network devices to obtain digital certificates without running any domain credentials. It is one of the role services on the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) within Windows Server environments, starting from Windows Server 2008 R2 onwards. NDES provides secure communication for network devices that lack traditional domain credentials.
Network Device Authentication Challenge and NDES Integration
Various network devices, such as routers, firewalls, and switches, depend heavily on internal software to manage network traffic. Most of the time, these devices do not have the capability to retain domain credentials, which are utilized for user authentication on computers. Lacking this functionality causes a problem establishing secure communication channels within the network. NDES is designed to address this challenge by using the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP), by bridging the gap between network devices, which helps to secure the communication process. SCEP establishes a secure communication protocol between NDES, operating as the Registration Authority (RA), and network devices. The SCEP protocol allows devices to request and obtain digital certificates from a designated Certification Authority (CA) server.
Benefits of Utilizing NDES
- Network Security: NDES establishes secure communication between network devices by issuing digital certificates. These certificates verify the identity of the network devices, which helps to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches in the network.
- Device Management: It also simplifies the process of network device enrollment for certificate-based authentication, allowing Administrators to manage certificates through NDES centrally, and therefore, reduces the need for manual configuration on individual devices.
- Scalability: NDES is designed to handle certificate enrollment for a large number of devices. This functionality makes NDES ideal for managing extensive network environments.
NDES Enrollment Process
The NDES enrollment process involves several key components:
- Device/Client: Clients are the network devices (router, switch, etc.) that require certificates.
- NDES Server (RA): The Registration Authority (RA) acts as an intermediate server, which bridges the communication between the client device and the Certification Authority.
- Certification Authority (CA) Server: The CA server issues certificates based on predefined policies and validates device requests forwarded by NDES.
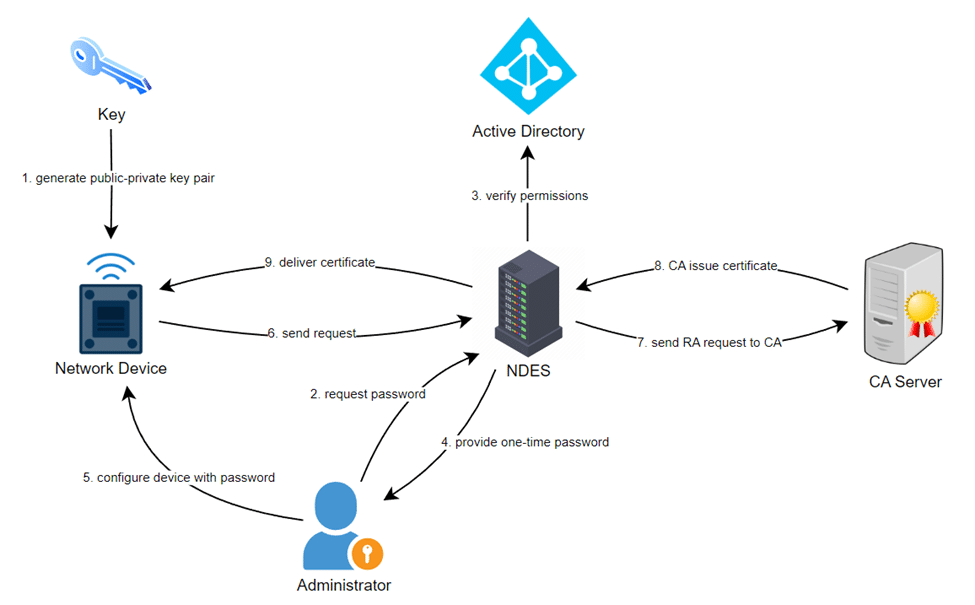
The overall enrollment process includes:
- Key Generation: Initially, a public-private key pair is generated on the network device.
- Password Request: The administrator requests a one-time password from NDES.
- Check Permissions: NDES verifies the request and checks for administrator’s permissions with the Active Directory.
- Password Delivery: If verification is successful, the NDES server provides a one-time password to the administrator.
- Device Configuration: The administrator configures the device with the password and sets it to trust the organization’s PKI.
- Enrollment Request: Once, the device is set-up, it sends an enrollment request to the NDES server.
- Request Forwarding: NDES acknowledges the enrollment request and forwards it to the CA server.
- Certificate Issuance: The CA validates the request and issues a certificate for the device.
- Certificate Retrieval: NDES receives the certificate from the CA and delivers it to the device.
NDES Security Best Practices
-
Lock down the server using Security Configuration Wizard
The Security Configuration Wizard will recommend locking down IIS and other services installed on the NDES server.
-
Ensure system hardening
Reduce the number of local admins groups to include only PKI Admins. Only members of the PKI Admins group are granted any logon user rights (interactive, remote interactive, log on as a batch job, log on as a service).
-
Create extended validity period device certificates
The default IPsec (Offline Request) certificate template has only a one-year validity period. If you define custom signing, encryption, or general-purpose certificate templates, consider creating a version 2 certificate template with a two-year validity period. A longer validity period reduces the management overhead for requesting device certificates.
-
Disable the NDES service when not in use
Stopping the NDES service ensures that unauthorized certificates will not be issued. Stopping the service also ensures that all data, such as all passwords that were not used by network devices, is cleared from the service cache.
Conclusion
NDES plays a vital role in securing network communication by enabling network devices to obtain digital certificates. By using SCEP, NDES provides a practical and easy-to-use solution for centralizing certificate enrollment, making the network more secure and reliable.
Encryption consulting provides expert support for NDES deployment and management, ensuring seamless integration and optimizing network security.

