- What is SOC 2 Compliance?
- Trust Service Criteria (TSC)
- SOC 2 Reports
- What is a SOC 2 Audit?
- Who needs an SOC 2 report?
- Importance of SOC and its benefits
- Roadmap to SOC compliance
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- How can Encryption Consulting help?
- Conclusion: Embracing SOC 2 as a Continuous Journey
SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls 2) is a widespread auditing standard developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). SOC 2 is designed to instill trust and ensure vigorous data security. SOC 2 helps to evaluate how effectively an organization’s information security policies and controls protect sensitive data.
As companies are depending on cloud-based services and third-party vendors to host critical information, SOC 2 provides a set standard for safeguarding that information. SOC 2 compliance is the most widely recognized form of cybersecurity audit, and many organizations use it to demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity. A standardized auditing standard that can be used to assess and verify the security practices of these service providers has become crucial.
A SOC 2 audit examines the organization’s controls that protect and secure its system or services used by customers or partners. The security posture of your organization is assessed based on the requirements outlined in the SOC 2 framework, known as the Trust Services Criteria (TSC). SOC 2 compliance is a minimal requirement for security-conscious businesses when considering a SaaS provider.
What is SOC 2 Compliance?
SOC 2 is a rigorous, principles-based compliance framework developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to assess how service organizations, particularly SaaS providers, cloud vendors, and data processors, manage and protect customer data. Unlike regulatory mandates such as GDPR or HIPAA, SOC 2 is a voluntary but highly respected standard focusing on security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy through its Trust Services Criteria (TSC).
In contrast to conventional cybersecurity frameworks, which offer general recommendations for security procedures, SOC 2 specifically assesses how well controls related to operational transparency and consumer data management are functioning. The framework is designed specifically for cloud-based and technology organizations, ensuring they retain operational transparency through independent third-party audits and use robust security controls (such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection).
Additionally, SOC 2 emphasizes risk management and control effectiveness, providing organizations with a structured approach to enhance their governance and operational integrity. SOC 2 reports come in two types: Type 1, which evaluates the design of security controls at a single point in time, and Type 2, which assesses operational effectiveness over 6–12 months, making it the gold standard for enterprise trust.
Trust Service Criteria (TSC)
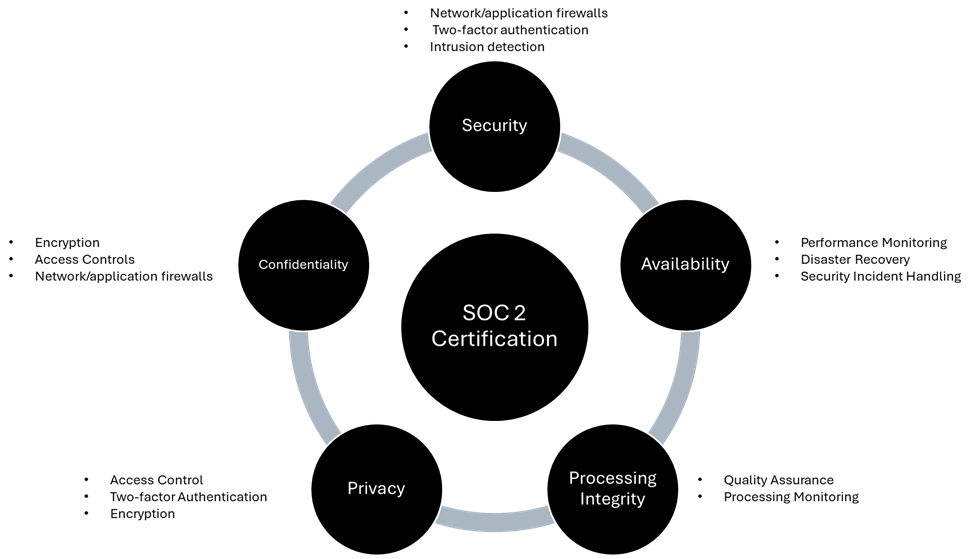
SOC 2 reports assure customers and stakeholders that an organization has implemented effective controls aligned with the five Trust Services Criteria (TSC). It is important to note that only security is mandatory among the following criteria.
- Security: Protecting against unauthorized access and ensuring systems and data integrity.
- Availability: Ensure that systems are up and running when users need them, with as little downtime as possible.
- Privacy: Protecting all personal and sensitive information by complying with all necessary data protection policies and legislations.
- Confidentiality: Preventing the disclosure of sensitive data without authorization at any point in time.
- Processing Integrity: Ensures system processing is complete, valid, accurate, and authorized.
The Five Trust Services Criteria are explained below:
Security
The fundamental principle of SOC 2 is security, which is required for each SOC 2 audit and guarantees that systems are protected from logical and physical intrusions. Control policies within your firm must be in place such that unauthorized users, both internal and external threats, do not gain access to data or systems. A complete security plan uses detective controls, like monitoring software that detects and warns users of potential intrusions, and preventive controls, like firewalls that deny unauthorized access.
Key controls
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires people to prove their identity in multiple ways (an example is a password + confirmation code sent to their phone) and greatly decreases the chance of unauthorized entry.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Giving access to resources based on job roles and requirements ensures that employees only have access to data needed for their work.
- Encryption: Data must be encrypted at rest and in transit using strong cryptographic methods like AES-256.
- Vulnerability Management: Regular vulnerability scans and patching help identify and remediate security weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert security teams.
Availability
Availability ensures that systems are operational and accessible as agreed upon in service-level agreements (SLAs). This criterion encompasses the infrastructure needed to support continuous operations and the incident response planning to address potential disruptions. Customers expect your services to be reliable and available when needed. When systems are down, it can interfere with a business and negatively impact client trust.
Key controls
- Redundant Infrastructure: Using several cloud regions or data centers to ensure failover if one site goes down.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) Plans: Document procedures to recover systems quickly after outages or disasters.
- System Monitoring: Constant observation of the uptime and performance of the system.
- Capacity Planning: Making sure one is well aware of the infrastructure’s capacity, such that heavy traffic loads won’t cause the infrastructure to fail or slow down.
Processing Integrity
Processing Integrity ensures system operations are complete, valid, accurate, timely, and authorized. All data processed in your system needs to be processed exactly as intended, and no errors should exist in the data that was processed, indicating the need for data validation and end-to-end transaction validation. This criterion ensures that input and output data will be consistent throughout the processing lifecycle.
Key Controls
- Input Validation: Techniques to ensure that all the data entered into the system is correct and complete.
- Error Handling: Procedures to identify, report, and resolve processing errors.
- Audit Trails: Audit logs capture the transactions and changes to data and allow it to be traced.
- Change Management: Processes to formally manage software updates and configuration changes.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality refers to the protection of confidential data from unauthorized disclosure. Organizations must protect confidential information such as intellectual property, trade secrets, or sensitive customer data. Confidentiality requires implementing comprehensive access control measures, such as RBAC or least privileged access, and enhanced encryption practices to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
Key Controls
- Data Classification: Regulations categorize data based on sensitivity levels.
- Access Restrictions: Ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Encryption: Safeguarding private information in transit or at rest.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): These are legal agreements with employees and parties to prevent information sharing without authorization.
Privacy
Privacy has to do with how personally identifiable information (PII) is collected, used, retained, disclosed, and obsoleted within the framework of privacy laws. New regulations such as GDPR and CCPA impact organizations in the responsible use of PII, which ultimately protects individuals’ rights and provides transparency. Adherence to these legislations keeps firms out of legal trouble and builds customer trust by demonstrating a commitment to privacy.
Key Controls
- Data Minimization: This is gathering only the information the firm requires for its operations. It is an excellent practice that complies with GDPR’s limitations on gathering data outside what is required.
- Consent Management: CCPA and GDPR mandates obtaining and documenting user consent for data collection and processing.
- Access Controls: Prevent unauthorized access to secure PII by restricting access to PII to authorized personnel only.
- Data Retention and Disposal: Securely delete data when no longer needed in compliance with regulations that mandate the timely disposal of personal data to minimize risk.
SOC 2 Reports
SOC 2 Report Types: Type 1 vs. Type 2, each serving different purposes:
| Report Type | Description | Audit Period | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Evaluates the design of controls at a specific point in time | Point-in-time (e.g., a specific date) | Useful for organizations seeking initial validation that controls are in place |
| Type 2 | Evaluates the operating effectiveness of controls over a period | Typically, 6-12 months | Demonstrates sustained compliance and operational maturity, including testing operating system effectiveness over time. |
Consider your goals, cost, and timeline constraints to choose between the two.
A Type I report can be faster to achieve, but a Type II report offers greater assurance to your customers. Many startups begin with Type I and move to Type II later.
What is a SOC 2 Audit?
A SOC 2 audit thoroughly evaluates an organization’s information security practices, focusing on the effectiveness of its controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Conducted by an accredited CPA, the audit assesses how well the organization protects customer data and ensures compliance with the Trust Services Criteria.
Before the formal audit, organizations often engage in a “readiness assessment” phase. Conducting pre-audit assessments helps identify issues with controls and areas to be improved so that organizations can solve those issues before the audit, which is important when organizations are at risk. Tools such as Vanta and Drata are available to help with continuous monitoring. These tools automate compliance tracking processes and yield better info on security practices in real-time, showing the organization’s controls as they are maintained, providing evidence of compliance in an audit.
The audit process involves a series of important steps. The first step is to define the scope of the audit, which sets the boundaries for what will be examined. Next, a gap analysis is conducted to identify discrepancies between current practices and the desired standards. As the audit unfolds, auditors often use sampling methods to evaluate how well controls work. They look at a representative selection of transactions or processes to ensure everything functions as it should.
The SOC 2 audit report offers valuable insight into an organization’s control environment, and it helps to build trust with clients or stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to data security and operational integrity. This audit is particularly relevant for service organizations that handle sensitive information, such as software-as-a-service (SaaS) providers, data centers, and managed service providers (MSPs).
Key Components of a SOC 2 Audit
- Third-Party Evaluation: To ensure objectivity and credibility in the evaluation process, the audit is carried out by an independent third-party auditor, usually an authorized CPA firm.
- Trust Services Criteria (TSC): The audit assesses the organization based on the five Trust Services Criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Each of these criteria focuses on different aspects of data management and protection, ensuring that the organization undergoes a thorough review of its controls.
- Types of Reports: The two main types of SOC 2 reports are Type I and Type II. A Type I report assesses the design of controls at a specific point in time. In contrast, a Type II report evaluates the operating effectiveness of those controls over a defined period, usually between three and twelve months. Type II reports provide a deeper level of assurance to clients and stakeholders.
- Audit Process: The audit process involves several stages, which include;
- Preparation: Organizations often undergo a readiness assessment to identify and remediate control gaps before the formal audit begins.
- Fieldwork: The auditor collects evidence and conducts interviews to understand the organization’s processes and controls.
- Reporting: After the fieldwork, the auditor prepares a detailed report that outlines the findings, including any deficiencies and recommendations for improvement.
The major deliverables of this process are logs, system configuration, and screenshots, which are presented as evidence.
After the audit, the auditor writes a report about how well the company’s systems and processes comply with SOC 2. Every organization that completes a SOC 2 audit receives a report, regardless of whether they passed the audit.
Here are the terms auditors use to describe the audit results:
- Unqualified: The company passed its audit.
- Qualified: The company passed, but some areas require attention.
- Adverse: The company failed its audit.
- Disclaimer of Opinion: The auditor doesn’t have enough information to make a fair conclusion.
Who needs an SOC 2 report?
A SOC 2 report is crucial for service organizations that store, process, or transmit sensitive customer data, as it showcases their dedication to security and privacy. For instance, a fintech company utilizing AWS would require a SOC 2 report to reassure clients that their data is managed securely and meets industry standards.
This report is especially important for organizations dealing with sensitive or confidential information, as it helps build trust with clients and stakeholders, implying that they prioritize data protection and compliance. Here is a detailed explanation of who needs a SOC 2 report and why:
Saas and Cloud Service Providers
1. Service Organizations Handling Customer Data
Any organization that provides services involving customer data, whether storing, processing or transmitting it, is a candidate for SOC 2 compliance. This includes a broad range of companies that act as service providers to other businesses and must prove their security posture to customers.
Why: Customers demand assurance that their information is processed securely. A SOC 2 report offers third-party confirmation that an organization’s controls comply with high security and privacy requirements.
2. SaaS companies
SaaS businesses are one of the most typical organizations requiring SOC 2 reports.
Why: These companies deal with sensitive customer data and infrastructure. The sensitive data could include financial, personal, and operational information. Complying with SOC 2 enables them to establish strict internal security controls, build trust, and meet enterprise customer requirements.
Regulated Industries
1. Financial Services and Fintech Companies
Financial institutions handle sensitive financial data, including transactions, account information, and personal financial records.
Why: Due to the high regulatory scrutiny and risk of financial fraud, SOC 2 reports assure that controls are in place to protect sensitive data throughout its lifecycle. Many enterprise customers require SOC 2 compliance before engaging with financial service providers.
2. Healthcare Service Providers and Health Tech Vendors
Healthcare organizations manage protected health information (PHI), subject to strict privacy laws like HIPAA.
Why: While HIPAA governs patient privacy, SOC 2 fills security gaps by ensuring healthcare technology vendors and service providers implement robust controls over data security, confidentiality, and availability. Hospitals and insurers often require SOC 2 reports from their vendors.
3. Companies in Education, Banking, and Other Regulated Industries
Healthcare organizations manage protected health information (PHI), subject to strict privacy laws like HIPAA.
Why: These types of businesses are exposed to increasing cybersecurity threats and regulatory scrutiny. SOC 2 is valuable for showcasing security efforts to customers and regulators. SOC is often contractually required in enterprise vendor onboarding.
Infrastructure Providers
1. Data Centers and Infrastructure Providers
Organizations that operate data centers or provide core infrastructure services play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive customer information. They are expected to implement strong physical and digital security measures to protect against unauthorized access and disruptions.
Why: These providers handle vast volumes of confidential data. Clients rely on them to protect this data from breaches and ensure that systems remain up and running without interruption.
2. Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
Because MSPs act as an extension of their clients’ internal teams, any security lapse on their part can directly impact the clients they serve. This elevated level of access puts them in a critical position of responsibility, as they help manage and secure IT environments across multiple organizations.
Why: A security breach at an MSP can potentially put all its customers at risk. SOC 2 compliance demonstrates the MSP’s commitment to safeguarding customer environments and is a good market differentiator.
Importance of SOC and its benefits
SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls 2) is an essential compliance framework for organizations that manage or process customer data, especially in the service sector. SOC 2 is important as it can provide assurance to clients and stakeholders that an organization is committed to maintaining high data security and operational integrity standards.
Importance of SOC 2
- Demonstrates Commitment to Data Security: SOC 2 assures that the firm has implemented robust controls to protect customer data from breaches, unauthorized access, and other risks. It is particularly critical for service providers like SaaS companies, cloud vendors, and managed service providers (MSPs) dealing with sensitive client information.
- Meets Enterprise Customer Requirements: Over 73% of companies request SOC 2 reports before onboarding vendors. There is a need to secure clients’ contracts, especially in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
- Centralized Security Management: SOC 2 compliance encourages organizations to strengthen their security controls and processes, providing a centralized method of controlling and demonstrating the effectiveness of their security posture.
- Provides Assurance through Independent Audit: SOC 2 reports are issued after an independent audit by a certified public accountant (CPA), assuring customers and stakeholders of confidence in the security controls and processes of the organization.
Benefits of SOC 2
- Enhanced Security Posture: Mandates like encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and intrusion detection systems are needed by SOC to enhance protection against vulnerabilities and cyberattacks.
- Competitive Differentiation: A clean SOC 2 report distinguishes organizations from their competitors, signifying maturity of operations and reliability. This is particularly important for SaaS providers and MSPs in highly competitive environments.
- Increased Customer Trust: With an independent audit, an organization gets an opportunity to showcase its commitment towards data security, which can enhance customer trust and client retention rates.
- Support Regulatory Compliance: While SOC 2 is not a regulatory requirement, it helps organizations comply with many compliance standards and industry best practices.
- Facilitates Vendor Management: SOC 2 reports provide standardized evidence of security controls, simplifying the process of vendor evaluation and due diligence for enterprise customers.
Roadmap to SOC compliance
SOC 2 compliance is a process that involves multiple teams and processes. It is a repetitive process because SOC 2 is a journey and not a checkbox to be ticked. Here’s a detailed breakdown:

Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
Before diving into compliance, clarify what you want to achieve and which systems or services are in scope. For this, you can refer to the AICPA’s guidelines directly.
- Identify critical systems: Which applications, infrastructure, or data stores handle customer data?
- Select relevant criteria: While security is mandatory, you may include availability, confidentiality, processing integrity, or privacy based on your business.
- Set goals: Are you aiming for a Type 1 report as a first step or a full Type 2 audit?
Step 2: Conduct a Gap Analysis
Assess your current state against SOC 2 requirements to identify areas needing improvement. For proper gap analysis, with complete assessment, gap identification, and actionable remediation steps, it is best to seek help from third-party consultants like us, Encryption Consulting.
- Review existing policies: Have you documented security policies, incident response plans, and access control procedures?
- Evaluate technical controls: Are your systems encrypted? Is MFA enabled?
- Interview stakeholders: Observe how daily operations are carried out.
- Document gaps: For instance, you may discover that backups are not properly encrypted or that accounts/accesses belonging to fired personnel are not immediately disabled.
Step 3: Develop Policies and Controls
SOC 2 requires documentation of controls in a formal format. It is recommended that security standards like NIST, CSF, or CIS be used as a reference for establishing such policies and controls. This includes:
- Access Management: Document how users get, modify, and lose access. Document RBAC models and MFA requirements.
- Incident Response: Document procedures for detection, reporting, and response to security incidents, including customer notification schedules.
- Vendor Management: Set up processes to evaluate third-party risks, including questionnaires and contractual clauses.
- Change Management: Define how software and infrastructure changes are approved, tested, and documented.
Step 4: Implement Technical Safeguards
To effectively convert policies into actionable technical controls, organizations can do the following:
- Deploy monitoring tools: Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to gather and assess logs for possible malicious behavior.
- Encrypt data: Deploy industry-standard encryption on network traffic, databases, and backups to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Configure firewalls and network segmentation: Deploy firewalls and network segmentation to limit lateral movement in your network.
- Schedule penetration testing: Schedule penetration testing regularly to identify vulnerabilities in your applications and systems proactively before they become incidents.
- Automate patch management: Implement automated patch management solutions to ensure timely operating system and application updates. This works to reduce the risk of exploiting through unpatched vulnerabilities.
Step 5: Perform Readiness Assessments
Internal or “mock audits” must be conducted ahead of the official audit to ensure compliance with controls and SOC 2 requirements. Organizations may also consider working with a pre-audit firm or using a platform that simulates audit requirements to better prepare for the actual audit process. This proactive measure can help identify gaps and enhance the overall compliance position.
- Test user access: Verify access rights are appropriate and revoked when employees leave.
- Restore backups: Check backup integrity by performing test restores.
- Review logs: Ensure logging is enabled and logs are maintained per policy.
- Simulate incidents: Conduct tabletop exercises to measure incident response success.
Step 6: Engage a Qualified Auditor
Choose an independent CPA firm with appropriate SOC 2 audit experience in your industry.
- Request proposals: Compare auditor expertise, fees, and schedules.
- Prepare documentation: Provide policies, system diagrams, user access lists, and evidence of control operation.
- Clarify expectations: Understand the audit scope, sample sizes, and evidence requirements.
Step 7: Execute the Formal Audit
The audit process varies by report type:
- Type 1: Auditor reviews control design and implementation simultaneously.
- Type 2: Auditor tests control effectiveness over a period (usually 6 months).
Step 8: Tackle Audit Findings
The auditors can highlight weaknesses or gaps in your security controls in their report. Here’s how to handle that:
- Prioritize remediation: Highlighted issues and gaps should be fixed based on the severity of the risks.
- Document fixes: Make sure to update your policies, apply any necessary technical patches, or improve your processes as needed.
- Communicate with stakeholders: Keep everyone informed about the progress of your remediation efforts, including updates on timelines.
Step 9: Maintain Continuous Compliance
SOC 2 is not a one-time event but an ongoing commitment.
- Automate monitoring: Use compliance automation tools like Drata, Vanta, or Secureframe to collect evidence continuously.
- Regular training: Educate employees on security best practices and phishing awareness.
- Periodic reviews: Update policies annually or after major changes.
- Incident response drills: Conduct tabletop exercises to keep teams prepared.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
1. Treating SOC 2 as a Checkbox Exercise
Some organizations look at SOC 2 as merely passing the audit and have a low priority on improving their security stance.
Solution: Embed security into your culture. Make penetration testing part of the development cycle and use SOC 2 as a guide to improve security, not just as a report.
2. Cross-Departmental Coordination
SOC 2 encompasses various departments, including HR, Legal, IT, and Operations, which can result in a lack of collaboration between them.
Solution: Appoint a compliance officer or a team. Collaborative tools like Jira and Confluence can be used to bring all the documentation and tasks into a single location. Conduct regular inter-departmental meetings.
3. Evidence Collection and Documentation
Finding, gathering, and documenting audit evidence can be confusing and time-consuming.
Solution: Automate collection wherever feasible. Use compliance platforms that can connect with your cloud and IT infrastructure to automatically retrieve logs, user access details, and configuration snapshots.
How can Encryption Consulting help?
In our advisory services, we provide detailed assessments, pinpoint gaps, and create action-driven, comprehensive roadmaps, helping you identify risks, align with regulatory changes to meet critical compliance requirements, and strengthen your security posture with expert guidance at every stage.
We focus on reviewing the policies you have in place, assessing your infrastructure, and identifying any gaps in your cryptographic environment that fail to meet the requirements of compliance. We work by understanding the capacity and limitations of your system, tailoring recommendations to fit your goals, and building roadmaps by estimating cost, resources, and timelines to help you meet all the requirements for SOC 2 compliance.
Conclusion: Embracing SOC 2 as a Continuous Journey
SOC 2 compliance is a comprehensive framework that enables enterprises to demonstrate their commitment to security, privacy, and operational excellence. SOC 2 can be turned from a compliance obstacle into a competitive advantage by understanding the Trust Services Criteria, which can help properly plan your audit, establish robust controls, and encourage a continuous improvement culture.
This blog provides fundamental knowledge and practical suggestions for effectively navigating the SOC 2 path, regardless of whether you’re an established company maintaining a Type 2 report or a startup getting ready for its first Type 1 audit. At Encryption Consulting, we provide businesses with expert guidance and practical solutions that can help you navigate the complexities of compliance and security such as SOC 2. Please reach out to us at info@encryptionconsulting.com for further information about our service.
- Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
- Step 2: Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Step 3: Develop Policies and Controls
- Step 4: Implement Technical Safeguards
- Step 5: Perform Readiness Assessments
- Step 6: Engage a Qualified Auditor
- Step 7: Execute the Formal Audit
- Step 8: Tackle Audit Findings
- Step 9: Maintain Continuous Compliance




