Introduction
In today’s world, all the applications or software utilized by users are virtualized and downloaded from a docker container. One fear many users have is that it might be possible that attackers tampered with the file that users are downloading from the container and have injected a malicious script or malware in it. If this is the case, whenever any person downloads and executes it in their system, the system gets affected by the attacker’s malicious script.
The Necessity for Docker Image Signing:
If an organization is providing a software/product to their customer, then how can the customer verify it is not tampered with? To provide customers with peace of mind on this subject, an organization can put their trusted signature on the software/product. If someone tries to tamper with the code, the signature gets changed. This is where image signing comes into the picture. Image signing is where an organization can sign their image before they push it to the container so that the customer can use it safely.
Similar to how malicious activity can be caught by code signing, when a user tries to install or execute the file, the signature will first be verified. If the organization’s image signing certificate is not found then it will stop the user from proceeding.
What is Docker Image Signing?
Docker image signing is the process of digitally signing docker images to confirm the software author’s identity and provide assurance that the code has not been altered or compromised.
How does Docker Image Signing work?
The way image signing works can be broken into two parts:
- At the server or developer side
- At the client side
Firstly, we’ll discuss how the
process takes place on the server side:

- The original image, i.e., the docker image the user wants to provide to customers safely, is firstly hashed by a hashing algorithm, because it’s practically impossible to reverse a hash.
- The hashed docker image we get is then signed by the private key of the developer.
- The signed hash docker image is then packed with the original image and digital certificate, which together are also known as an image signing certificate.
- Now, it can be uploaded or transferred to the customer.
Now, let’s go through how the process takes place on the client side.
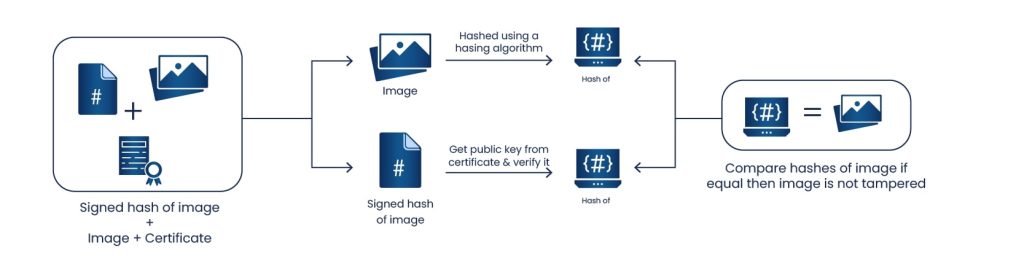
- The original docker image is passed through a hashing algorithm, to get the hash of the image.
- The public key is extracted from the certificate and applied to the signed hash of the docker image to extract the hash of the image.
- Both the hashes created from steps 1 and 2 are compared, and if both the hashes are the same then the image has not been changed and the signature is considered valid.
- At the same time, the image signing certificate is checked to ensure it was signed by a trusted CA. The expiry date of the image signing certificate is checked, and certificate is also checked against the revocation lists to ensure it is valid.
Weaknesses of Docker Image Signing
There are several weaknesses to image signing, as well, including:
Improper management of the private key created at the beginning of the Image signing process can result in insecurity of the software being sent. If a legitimate private key is stolen, then the attacker can encode their malicious software with the private key, which will tell the user that the software is safe to use, even if it isn’t.
Threat actors can obtain a trusted certificate, but what deters most attackers is the need to provide identification information to obtain a certificate. If malicious software is distributed with a legitimate certificate, the developer can be identified and stopped.
Note: If the user allows the installation of the software, even if the Operating System says it is not a signed image, then image signing is rendered useless.
To prevent these weaknesses, there are best practices that should be followed:
For the protection of encryption keys, Hardware Security Modules, or HSMs, should be used. An HSM is a specialized, highly trusted physical device. It is a network computer that performs all the major cryptographic operations including encryption, decryption, authentication, key management, key exchange, etc. They are tamper-resistant and use extremely secure cryptographic operations.
Along with HSMs, the principle of least privilege should be used with keys, to ensure only users who need the key have access to it.
Finally, caution should always be used with image signing. Only download and install software that is image signed by a trusted CA.
Future of Code Signing
As we can see in today’s world, security and trust are a major part of any organization to growth. Every organization wants to save its data and provide secure data to its clients. Various malicious activities are occurring daily, so image signing is going to increase exponentially. Every organization needs to put code signing and image signing into practice.
Our offering of Code Signing
Our product, CodeSign Secure, provides a secure and flexible solution to an organization’s code signing needs for signing Windows, Linux, Macintosh, Docker, and Android/iOS apps.
Our framework can be extended to protect any other code or document as requested by our customers.
- The keys are protected by your choice of HSM, – nCipher, Utimaco, Safenet.
- Policies and workflows are defined to secure and streamline your job submission and approval process.
- Your existing virus and malware scans can be integrated systematically.
- Developed on an open REST API, allowing for custom integrations and requirements.
Conclusion
Data is crucial in this connected world, where code signing can be used for the verification of data. Tampered data can lead to a severe loss and thus should not be trusted. Software should also show a warning or completely block the user from installing software with untrusted certificates. A signed software or application can achieve a trusted network of users, devices, and programs.




