Secure communication is essential in today’s world, and Trust stores play an important role in ensuring this. A trust store is a digital repository that stores certificates from verified sources.
When we visit a website and see a secure lock icon, it’s a sign that we are connected to a secure network. It’s because a complex system works behind the scenes. A trust store makes this system possible. But what exactly is a trust store, and how does it function?
Think of our friends on social media as a trust store. We only accept a friend request from someone we know or recommended by a trusted connection. Likewise, a trust store is a repository that holds onto digital certificates issued by the Certification Authority (CA) that our operating system or browser trusts. These certificates are like digital identification of the websites we visit and tell us whether the website is trustworthy or not.
Now, to get a better understanding, let us understand how the process of verification works:
-
Websites send digital certificates
When we visit a website, it sends a digital certificate to the browser.
-
Trust Store Checks the Certificate
The Trust store comes into play here; it verifies the digital certificate.
-
Is the certificate trustworthy?
If any CA signs the digital certificate on the trust store list, then the certificate is deemed trustworthy and hence the connection is secure.
-
Connection is Not Secure
However, if the certificate doesn’t match a known CA, the trust store throws up a red flag. This is when we see the “connection not secure” message.
Now, Operating systems and web browsers maintain a list of these certificates called trust stores. This helps implement strict criteria to determine which CA certificates are deemed trustworthy. Trust stores enable secure communication by referencing these certificates during any online interaction and help you avoid connecting with potentially malicious entities.
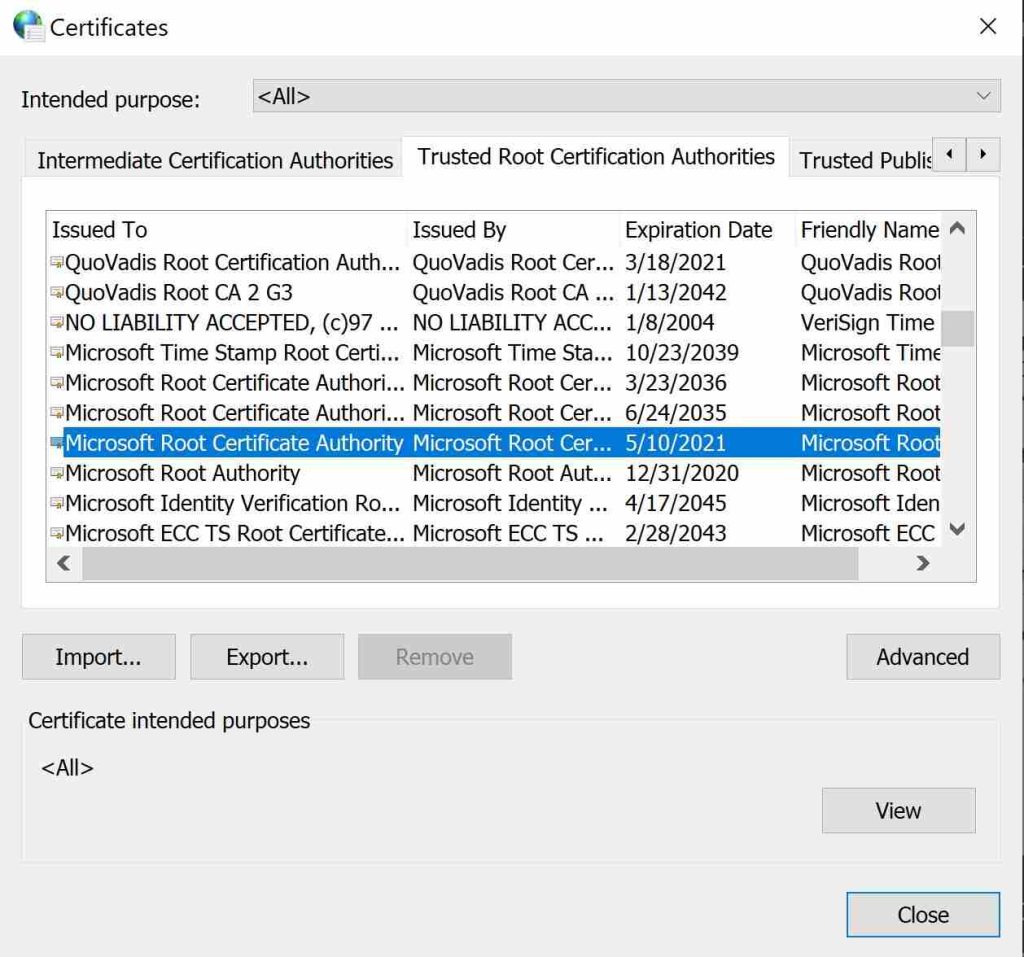
To see trusted root certificates on your Windows machines, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel.
- Click on “Network and Internet”.
- Select “Internet Options”.
- In the Internet Properties window, go to the “Content” tab.
- Click on the “Certificates” button.
- In the Certificates window, move to the “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” tab.
So now the question arises where this trust store comes from. There are four major organizations that maintain such trust stores.
- Microsoft root certificate program that is used by Windows.
- Apple root certificate program is used by all Mac devices.
- The Mozilla root certificate program is used by Mozilla itself and most Linux distributions.
- Google root certificate program used by google chrome and other applications.
Each of these entities has its standards and requirements for including a Root certificate in its trust store, but they all require a CA to undergo one or more audits before their Root certificate can be included.
Now, there are hundreds of CAs that are trusted by the CA/Browser Forum Baseline Requirements, which sets the rules that the trusted certificate authorities (CAs) are supposed to follow before issuing certificates.
Moreover, CAs are audited for compliance checks with these rules and protocols as part of the WebTrust audit program, which is required by some root certificate programs like Mozilla for inclusion in their trust stores.
The following table provides a breakdown of key aspects of the trust store.
| Aspect | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Trusted Root CAs | The number of Certificate Authorities (CAs) whose certificates are pre-installed and trusted by a specific trust store. |
|
| Frequency of Updates | How often the trust store is updated with new or revoked certificates? | Trust stores are updated on a weekly or monthly basis. |
| Types of Certificates Stored | The different types of certificates a trust store might contain, beyond just website certificates. |
|
| Common Verification Errors | Examples of errors a user might encounter if a website’s certificate doesn’t validate against the trust store. |
|
In this scenario, certificate authorities are considered trustworthy third parties when issuing digital security certificates like SSL, code signing, etc. They handle public keys and other encryption-related credentials. They also authenticate and associate websites, email addresses, businesses, and others with cryptographic keys.
The CA is responsible for verifying and issuing the organization’s data with distinctive certificates. These CAs are trusted to verify a website’s / organization’s legitimacy, and some researchers have pointed out that their role in this overall system could be a single point of failure. Moreover, if a CA is compromised, this essentially means that, theoretically, any attacker could issue fake certificates and exploit the trust store verification process.
Now, managing the intricate web of keys and certificates can be complex. Security researchers highlight this complexity as a potential vulnerability. Any errors or vulnerabilities in this process could create opportunities for attackers to exploit.
In order to resolve these issues, intricate solutions are generally in place, such as a certificate lifecycle management solution (CLM). A CLM could potentially help an organization manage its certificates.
Implementing a centralized CLM allows for better and centralized oversight and control over the entire certificate lifecycle. It helps the organization have better visibility of certificates, enforces standardized processes, tracks certificate usage, and promptly identifies and addresses any issues.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Trust stores play a crucial role in establishing a secure connection for any online interaction. They are like a secure vault that stores certificates from verified sources (Certification Authorities). This vault is used to verify a website’s identity. The process is like a digital handshake with confirmed credentials to ensure a secure and encrypted connection.
However, we must acknowledge that this process has inherent complexities. The high dependency on CA creates the potential for a single point of failure. Additionally, managing the web keys and certificates can create complexity and lead to vulnerabilities.
Moreover, to overcome these challenges, our CLM CertSecure could help manage these certificates and potentially solve the issues with oversight and complexities.
How can Encryption Consulting help?
Encryption Consulting provides specialized services tailored to identify vulnerabilities and mitigate risks by providing PKI Services. Our strategic guidance aligns PKI solutions with organizational objectives, enhancing efficiency and minimizing costs. By partnering with Encryption Consulting, organizations can unlock the full potential of PKI solutions, realizing tangible financial benefits while maintaining robust security measures.
Encryption Consulting’s PKIaaS provides a flexible and secure PKI solution tailored to your specific needs, offering benefits such as customizable options, high assurance standards, and a low-risk managed approach. PKIaaS automates key and certificate management tasks, reducing operational overhead and minimizing the risk of human error. Additionally, it enhances network visibility by requiring certificates for access. It will take care of building the PKI infrastructure to lead and manage the PKI environment (cloud/ hybrid or On-Prem) of your organization.
CertSecure Manager has a comprehensive suite of lifecycle management features. From discovery and inventory to issuance, deployment, renewal, revocation, and reporting. CertSecure provides an all-encompassing solution. Intelligent report generation, alerting, automation, automatic deployment onto servers, and certificate enrollment add layers of sophistication, making it a versatile and intelligent asset.