Understanding PKI and the Trends Driving Its Growth
Public key infrastructure (PKI) is a system for the creation, storage, and distribution of digital certificates which are used to verify that a particular public key belongs to a certain entity. The PKI creates digital certificates which map public keys to entities, securely stores these certificates in a central repository and revokes them if needed. The adoption of PKI has increased steadily over the years, with most analysts predicting 15% – 20% growth rates between now and 2024-2025. The broad reason for the steady adoption is not surprising: the increased digitalization of enterprises, consumers and society. However, since digitalization often means different things to different people, we look at some specific trends in digitization that are driving PKI usage and adoption.
- The Internet of Things (IOT): The IOT is emerging as one of the major factors driving PKI adoption. The number of connected devices already exceeds the number of human beings on the planet, and even conservative predictions indicate around 50 billion connected devices likely to be in place over the next five years. The proliferation of IOT devices along with the associated threats such as altering a device function, means that significant efforts are needed for IOT vulnerability management. PKI is expected to play a major role here since these devices will primarily rely on digital certificates for identification and authentication.
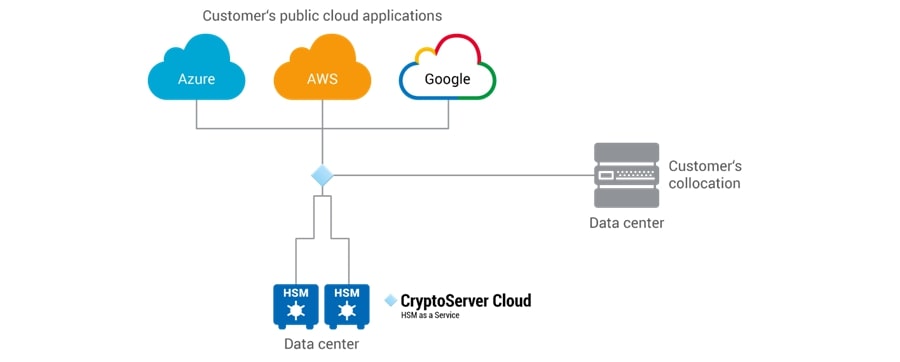
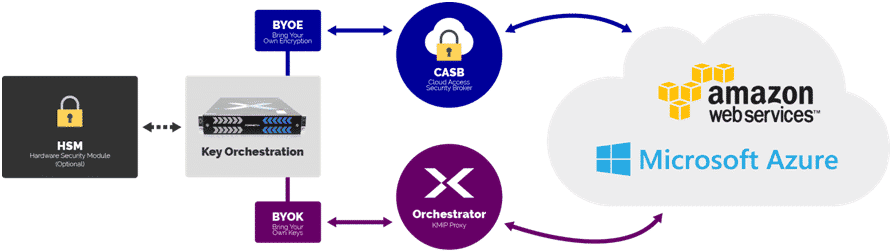
- Cloud applications and services: Cloud usage is truly mainstream today: A recent report from Flexera indicates that 94% of enterprises today leverage some form of cloud (public, private, hybrid) services. With organizations moving an increasing number of workloads to the cloud, the need for PKI credentials for cloud-based applications is going up correspondingly. Another overlap area between PKI and cloud technology is Certificate Authority (CA) services. These could be a public CA service such as those available from companies like Comodo, Symantec or GoDaddy; or they could be a private CA running in a public cloud; or a private CA running in a private cloud.
- Mobile applications: Smartphones and mobile applications are ubiquitous today. Both consumer mobile applications as well as enterprise mobility (e.g. BYOD or Bring Your Own Device) scenarios are driving PKI usage. No one can argue against the productivity gains and convenience workforce mobility provides. However, the challenges of mobile device management, especially from an authentication and data security perspective are often underestimated. Enterprises need a reliable method to verify the mobile user’s identity, validate the device itself, and secure the information through encryption. This is where digital certificates and PKI plays a big role.
- E-Commerce and web: One sector where the impact of digital disruptions has been extremely widespread, is retail. Online shopping has been a game changer for the retail industry. And though E-commerce sales are still under 20% of overall retail sales, every retailer today, big or small, needs to have an e-commerce presence. Also, the minute payments and financial transactions are involved, authentication and encryption services become critical. Over the years, one of the key enablers for the boom in the E-commerce industry has been PKI and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates, which have ensured the safety of online transactions. In general, security on the web has become such a necessity today that SSL support is now becoming de-facto for any website, not just e-commerce. Most major browsers immediately flag a website as “not secure” in the address bar, if an SSL certificate is not available. SSL also has a direct impact on search engine rankings – unsecure web sites typically rank lower than those using SSL. Apart from these, other trends driving increased PKI adoption across enterprises today include initiatives related to risk management, cost reduction, and compliance to the regulatory environment (such as digital signature legislations). One thing is clear – in an increasingly digitalized world, PKI literally holds the key to ensuring safe and secure transactions for enterprises and consumers worldwide.
2019 Rightscale State of the Cloud Report from Flexera