In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, where digital interactions have become the backbone of modern society, the vulnerability of even the largest tech giants has come to the forefront. Recent incidents involving industry titans like Microsoft and Cisco have highlighted the critical importance of managing digital certificates – the often-overlooked guardians of secure digital communication. These incidents are a stark reminder that no entity, regardless of size or stature, is immune to the far-reaching consequences of expired certificates.
Outages happen more often than we realize.
Many people might not know about digital identity certificates, but they definitely notice when organizations don’t handle them well. When a certificate expires, it stops secure connections. For example, if you try to use your banking website and the certificate is expired, your browser will stop you from accessing the site. You can’t use the service even if the bank’s servers are working.
Recently, some big companies have had problems because of certificate mistakes. Microsoft Teams didn’t work for about three hours in February because of an expired certificate. This affected people who use it for online meetings. Later, Spotify, a music streaming service, had a similar issue. People couldn’t listen to music for an hour. The problem was fixed after someone noticed an important certificate had expired.
These outages were short and not too bad, but that’s not always true. O2, a European mobile company, had an outage that lasted almost a whole day. It turned out that an expired certificate from a company called Ericsson caused the problem. O2 got around $132.8 million as compensation from Ericsson. This wasn’t the first time a big issue happened because of an expired certificate, but it was the one that made people realize how serious it can be, both for money and reputation.
Recently, California had a serious problem. They didn’t report all their COVID-19 cases because a certificate had expired. This messed up their system and caused a backlog. Certificates are super important for website and device security. Not handling them right can cause problems in the real world.
Microsoft Azure’s Widespread Outage: Unveiling the Chain Reaction
Microsoft Azure, a pioneering cloud computing platform, experienced a cascading disruption that sent shockwaves through the tech world. The root cause? An unexpected villain – expired SSL certificates. On a day when countless businesses and users relied on the Azure ecosystem, the oversight of these certificates led to a domino effect that affected many services.
The Impact
-
Operational Paralysis
The expiration of SSL certificates caused services to come to a grinding halt. Businesses relying on Azure’s
cloud
infrastructure found themselves in operational paralysis, unable to access essential tools and data.
-
Customer Downtime
The incident reverberated to end-users as well. Customers experienced frustration as applications and platforms
they
depended on were suddenly inaccessible.
The Solution
-
Proactive Monitoring
Implement a certificate management solution that tracks certificate expiration dates continuously. Regularly
audit
certificates to ensure timely renewals, preventing service disruptions.
-
Redundancy Planning
Develop redundancy plans to mitigate the impact of certificate-related outages. Implement redundant certificates
or
alternative solutions to maintain service continuity.
Cisco Webex Service Disruption: Unraveling Collaboration Challenges
Cisco’s Webex, a cornerstone of remote work and virtual collaboration, faced an unforeseen setback due to an expired SSL certificate. This event highlighted the vulnerability of even the most essential tools used for modern work dynamics.
The Fallout
-
Virtual Meeting Disruptions
The expiration of a crucial SSL certificate disrupted virtual meetings and collaborative sessions, undermining
the
seamless communication that businesses and individuals rely on.
-
Global Connectivity Impact
Users across the globe experienced connectivity issues, affecting their ability to communicate effectively and
jeopardizing workflow continuity.
The Response
-
Comprehensive Certificate Lifecycle Management
Establish a comprehensive certificate
lifecycle management process that involves regular audits, automated
renewal
notifications, and testing procedures to prevent such disruptions.
-
Robust Incident Response
Develop a well-defined incident response plan that outlines steps to be taken in the event of a
certificate-related
disruption. This includes communication strategies and action plans to minimize downtime.
Struggles with Managing Digital Certificates
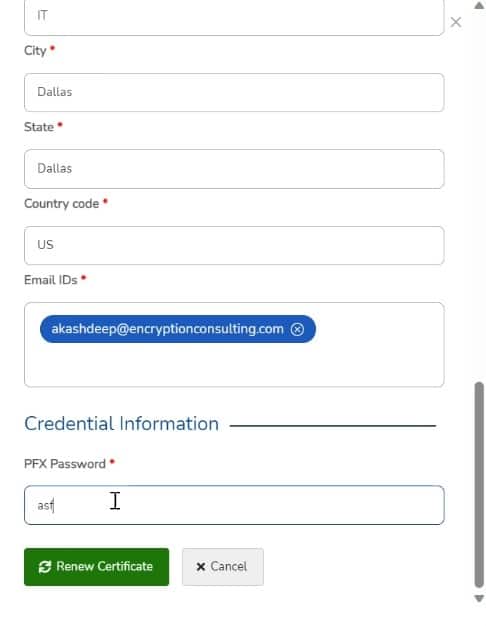
Taking care of digital certificates is essential to avoid costly problems with your online services. These certificates have a limited time. They’re valid; if you don’t watch them, your applications might stop working. If you miss important details like when a certificate expires or which device it’s connected to, you might not renew it in time, and your online service could go down.
Here are some reasons why digital certificates might not be managed well
-
Limited Visibility
It’s hard to keep track of all your certificates and their important details, like when they’ll expire or where
they are
on your network. This makes it tough to know if there’s a problem, fix issues, and stop your apps from crashing or
being
hacked.
-
Time-Consuming Manual Work
Doing things manually to handle certificates is slow and can easily lead to mistakes. Setting up certificates
manually
takes time, making your apps and devices slow. Renewing, revoking, and checking certificates manually can also
cause
your services to go down or be less secure.
-
Dealing with Many Certificates
If you have lots of certificates from different places, managing them gets complicated. Some certificates come
from
inside your organization, and some from outside have different expiration dates. This makes everything harder to
manage.
-
Not Ready for Changes
Doing things manually doesn’t work well when things change. If you need to update your setup or renew many
certificates
all at once, it takes too much time and planning. This leaves your certificates open to attacks, and your services
might
be vulnerable for too long. Also, you might not know your certificates’ security standards, making it hard to spot
problems and fix them quickly.
-
Cloud Confusion
With more certificates spread across different cloud services and devices, keeping track of them is tough. Old
tools and
manual work can’t handle this well so some certificates might get ignored. Attackers can then find these ignored
certificates and use them. Keeping track of certificates using spreadsheets across different clouds is risky for
your
business’s safety.
Impact of Certificates Expiring Unexpectedly
We have papers like driver’s licenses and passports with dates on them. When those dates pass, we can’t use them anymore. Digital certificates are like this for machines. They help machines identify themselves and work safely. But what happens when these certificates expire?
-
Unexpected Shutdowns
An unexpected shutdown means a system can’t do its main job. This might mean it’s offline or not working properly
because of an expired certificate. If certificates aren’t renewed on time, it can lead to the system going down.
This
happened to Starlink, causing problems for them.
-
Open to Hackers
Expired certificates that don’t follow security rules become open doors for hackers. Hackers look for these weak
points
to attack. They can do serious things like stealing data or tricking systems. Many companies use different
certificates,
and tracking them all is hard. Hackers are taking advantage of this chaos to carry out more complicated attacks.
-
Customers Lose Trust
When a website has an expired certificate, it shows a warning to users. It might say the site is not secure, or
attackers could be trying to steal info. Users will be worried and won’t trust the site anymore, even if there’s
still
some encryption going on.
-
Harm to Reputation
A bad reputation might not directly cost money but can hurt a lot. People won’t like it if a website keeps having
problems, warnings, and slow internet. This can especially be bad for big customers. They might leave, and that’s
a big
loss. This bad image can spread to the whole business, making it hard to get support and money.
Certificate Management
Prevent certificate outages, streamline IT operations, and achieve agility with our certificate management solution.
The Power of Automation in Handling Certificates
Think about all the devices, applications, and services you use. They all have special IDs to work safely. These IDs, called certificates, are like digital IDs for machines. They need to be managed properly to avoid problems. However, doing this manually is hard and doesn’t work well. This is why organizations need to use automation for certificate management.
When certificates expire, it can cause big problems. Imagine if your favourite app suddenly stopped working because of an expired certificate. This can be even worse for important services like Starlink. So, it’s really important to keep track of all your certificates, no matter where they are. This is especially true for cloud services, DevOps (development and operations) setups, and devices like smart devices.
Automating the process of managing certificates means making it easier and safer. It helps find certificates, keeps a list of them, renews them on time, and stops using them when needed. Google even wants certificates to last for a shorter time, so things could worsen if organizations don’t use automation.
The main idea of using automation for certificates is to ensure companies have control and know what’s happening with their certificates. This happens by putting everything in one place and using automation tools to manage certificates from start to finish. This makes sure the process is fast, easy, and secure.
There are important things to do with certificates, like getting new ones, renewing old ones, and stopping ones that are no longer needed. Doing these things right is key to managing certificates well. Automation tools help with this by giving one place to do everything with certificates. This way, you can do things quickly and avoid making mistakes. It’s like having a central control panel for certificates. This also makes it easy to follow the rules for how certificates should be used across all devices and setups.
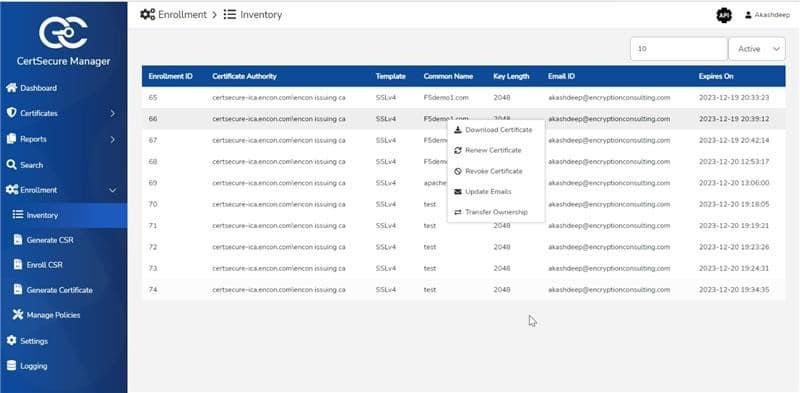
How can Encryption Consulting’s CertSecure Manager help?
Encryption Consulting’s CertSecure Manager plays a pivotal role in addressing and mitigating the risks associated with certificate expiry. In the realm of cybersecurity, digital certificates serve as fundamental components for ensuring secure communication, data integrity, and authentication across various digital platforms. However, when these certificates expire, it can lead to significant disruptions, vulnerabilities, and potential breaches.
CertSecure Manager offers comprehensive features designed to manage certificates throughout their lifecycle proactively. Here’s how it can help:
-
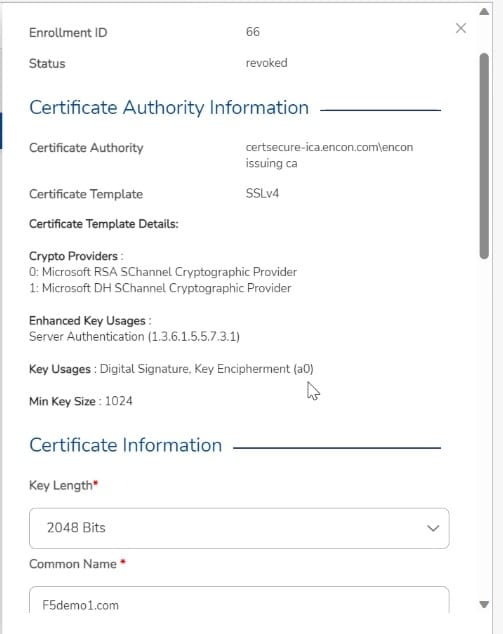
Certificate Monitoring and Alerting
The CertSecure Manager continuously monitors digital certificates’ expiration dates across an organization’s
infrastructure. It sends timely alerts and notifications to administrators, providing ample time for renewal
actions to
be taken.
-
Automated Renewal
Ensuring that certificates are renewed on time can be tedious, especially when dealing with many certificates.
CertSecure Manager automates the renewal process, reducing the risk of oversight and ensuring that critical
certificates
remain valid.
-
Centralized Management
Managing certificates across different systems and applications can be complex and error-prone. CertSecure
Manager
provides a centralized platform where administrators can view, track, and manage all certificates from a single
interface, enhancing efficiency and control.
-
Policy Enforcement
The solution allows organizations to define and enforce certificate policies. This ensures that certificates are
created
with proper configurations and adhere to security best practices, minimizing the chances of misconfigurations that
could
lead to vulnerabilities.
-
Risk Assessment
The CertSecure Manager performs regular assessments of the certificate landscape. It identifies potential
vulnerabilities stemming from expired or misconfigured certificates, enabling proactive remediation before
malicious
actors can exploit them.
-
Reporting and Auditing
Detailed reports are generated, providing insights into certificate statuses, renewals, and potential risks.
These
reports are valuable for compliance requirements, audits, and demonstrating a strong security posture.
-
Integration with Existing Systems
CertSecure Manager integrates with various certificate authorities, ensuring seamless integration with existing
certificate issuance processes.
-
Reduced Downtime
By preventing certificate expiry-related disruptions, CertSecure Manager maintains uninterrupted services and
reduces
downtime, ultimately enhancing customer trust and satisfaction.
-
Enhanced Security Posture
Expired certificates can create security gaps that attackers can exploit. By ensuring certificates are always
up-to-date, the CertSecure Manager contributes to an organization’s overall security posture.
Conclusion
Recent events with big tech companies like Microsoft and Cisco show digital certificates’ importance for online
security. These certificates are like behind-the-scenes protectors of our online activities. These incidents also
teach
us that not managing certificates properly can lead to serious problems.
In the digital world, where smooth communication and reliable services are crucial, companies need to understand how certificates work and take steps to avoid issues when they expire. By looking at these examples and using strong certificate management methods, companies can become stronger, keep customers happy, and confidently navigate the online world.