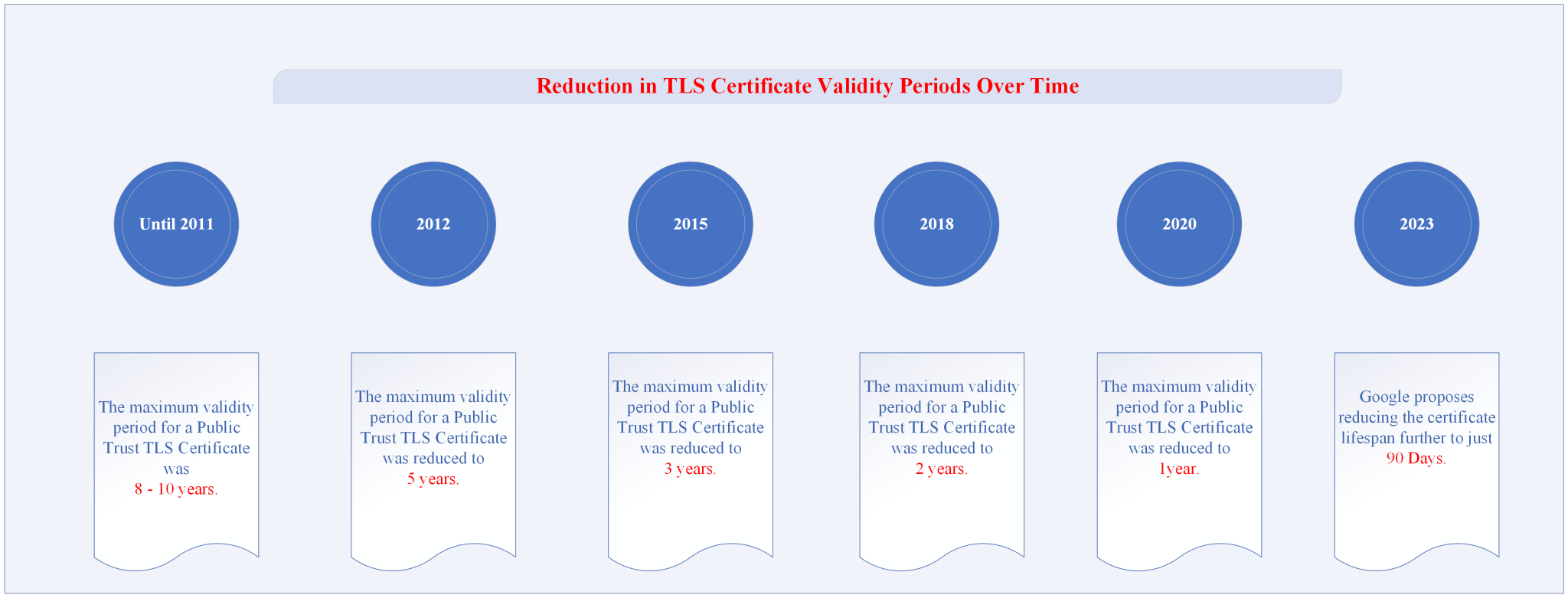
The NIS 2 Directive is a new EU-wide framework to improve cybersecurity among all member states. It strengthens EU cybersecurity by imposing strict security regulations and implementing incident reporting tasks for member states and companies. Addressing ICT supply chain security and resilience is consistent with the EU’s overall policy for a safe digital environment.
NIS 2, which was published on December 27, 2022, expands the scope of the 2016 NIS Directive to more industries. This means that more companies are expected to follow more challenging cybersecurity guidelines, which include improved encryption and data protection procedures. Most importantly, it specifies basic security and reporting criteria, making compliance straightforward for enterprises in different EU nations.
The directive focuses on protecting supply chains, enhancing the quality of incident reporting, and putting tougher control measures in place. Supply chains are among the basic activities every organization must carry out. They contain all the interlinked entities, positions, processes, data, and other assets used to provide products or services from the providers to the end customers. Enhancing the incident response system includes creating appropriate steps and timelines to alert relevant bodies on cyber security events. This enables effective mitigation of the threats. Strong regulatory guidelines and monitoring of all organizations are necessary for strict control methods.
This ensures that businesses meet cybersecurity standards and manage risks related to their activities and supply chains. To put it simply, NIS 2 seeks to provide a uniform degree of security throughout the EU, just like GDPR unified data privacy legislation. This means that any entity under the principles of NIS 2 must comply with the directive by setting up appropriate measures, including high-level management, monitoring, and control measures to protect its systems. If you are in charge of your company’s cyber security, then you should evaluate where you stand right now and prepare to meet the new, stricter requirements.
NIS2 is for European cybersecurity, exactly as GDPR was for European data protection.
New Organizational Requirements with NIS 2
1. Risk Management
Organizations should take the required steps to reduce cyber risks and consequences to comply with the new directive. Precautions like stronger network security, encryption mechanisms, supply chain security, access control, and incident management should be considered in time.
2. Reporting Obligations
Companies must create proper procedures to report security issues to the appropriate authorities accurately. NIS 2 has clear notification requirements, and major incidents must be notified within 24 hours.
3. Corporate Accountability
Under NIS 2, corporate management monitors authorizes and obtains training on all risks and security measures. Executive duties and responsibilities are greatly influenced by direct accountability such as this. Instead of assigning these responsibilities, it calls on leaders to actively monitor security protocols. Their defenses’ efficiency and dangers should also be well known to them. Executives should now take an active role in recognizing cyber threats and developing strategies to counter them. This moves them from passively monitoring the incidents that are reported to actively participating in risk management.
4. Business Continuity
Organizations must also think about business continuity planning to handle any risks brought on by major security events involving data breaches, supply chain threats, phishing, malware, or other social engineering schemes. Issues including system restoration, protecting essential services, and assembling a crisis management team should all be included in this strategy.
How does NIS 2 affect an organization?
Organizations are greatly affected by the NIS 2 Directive as it expands the scope of cybersecurity regulations to include more areas considered significant to the economy and society. NIS 2 has significantly influenced several industries, including healthcare, where protecting patient data is vital; financial services, which are necessary for maintaining economic stability; and energy, where cybersecurity is necessary for securing infrastructure.
Unlike its predecessor, NIS 2 coverage is increased as it aims to include many smaller and larger enterprises in various industries. Any business in the EU, including “all public and private entities across the internal market that fulfill important functions for the economy and society as a whole,” should employ suitable measures for creating secure infrastructure. Due to this new regulation’s complexity, firms must begin planning immediately to fully understand its scope and its effects on their operations.
NIS 2 differs from its predecessor in a few significant ways. To begin, NIS 2 sets stricter rules for risk management and incident reporting, requiring enterprises to do periodic risk assessments and report large events to authorities within a specific timeframe. This requires extensive incident reporting as well as an analysis of the ways in which incidents affect operations.
Executives may be held personally responsible for non-compliance as NIS 2 places a significant emphasis on management’s personal accountability. This was less clear in the earlier directive. For sensitive data to be adequately protected, organizations must also set up policies on cryptography and encryption.
Organizations must thus begin planning right now in order to properly understand the extent of NIS 2 and how it can affect their operations. While many businesses see compliance as only checking a box to satisfy the bare minimum, NIS 2 should be viewed as a starting point for reaching greater cybersecurity regulations.
This preventive strategy, aiming to increase resilience against cyber crimes, calls for a cultural shift toward compliance by having companies reconsider their cybersecurity policies, invest in new technology, and embed NIS 2 principles into their operational frameworks. Organizations that violate the new rules risk fines of up to €10 million, or 2% of global turnover for critical services, making non-compliance very risky.
This suggests that businesses have to stick to strict risk management protocols, which include conducting periodic risk evaluations and establishing effective security measures appropriate for their operational environments.
Tailored Encryption Services
We assess, strategize & implement encryption strategies and solutions.
NIS 2 – Actions to take now
1. Verify whether NIS 2 applies to your company
Businesses operating in the NIS 2-defined sectors need first to determine whether the regulations cover them, find whether they are regarded as essential or important, and understand their responsibilities regarding NIS 2-related obligations and how these will influence the present cybersecurity compliance framework.
This should take up the first week or two of your project and be done as a top priority.
2. Identify applicable Member State laws for your company
Once you have confirmed NIS 2 applicability, knowing the unique legal necessities in the Member States where you operate is important. This may modify operational choices and compliance plans. Businesses outside the EU that provide services within the EU must decide on a “Representative” based in one of the EU Member States in which they conduct business.
Once NIS 2 applicability has been verified, you should dedicate the second part of your project to this.
3. Determine if your business is subject to any new EU cybersecurity regulations
NIS 2 is part of the EU’s larger cyber regulations, and it is only one of several EU-wide cyber-related rules that in-scope firms must include in their compliance structure. Organizations will have to learn the interrelationships between the future EU data, cybersecurity, and technology regulations and the broader regulatory environment in order to develop and implement detailed compliance plans.
This step can be initiated simultaneously with the previous ones, but it might take longer to assess the interconnected standards, so dedicate the third phase of your project to this.
4. Evaluate your company’s incident response procedures
To ensure that data breaches are managed efficiently, it is crucial to assess your company’s incident response policies. Operational resilience and compliance depend on efficient incident response. Organizations should conduct realistic drills, give defined responsibilities, and confirm communication channels to increase readiness. To keep up with evolving threats and technical developments, they should also often review and update incident response protocols.
This step should come after the first evaluations of regulatory applicability and can be modified over time, committing the project’s fourth phase.
5. Review your company’s cybersecurity risk mitigation procedures
Review and update cybersecurity risk mitigation procedures frequently to stay ahead of evolving threats and vulnerabilities. Examine any weaknesses in the current risk management system and put proper measures in place to protect private information. Develop a culture of awareness and attentiveness among team members to increase cybersecurity resilience and lower risks.
Meeting NIS 2 Compliance with Encryption Consulting
As we go over the minimal steps you must do to comply with the NIS 2 complaint, let’s talk about how encryption consulting may assist you in meeting your compliance needs. We provide encryption assessments as part of our advisory services. With this service, we can help you become NIS 2 compliant. The evaluation brings up security flaws that require improvement and suggests measures to avoid them. We identify and understand your company’s present state of data security, including its abilities, challenges, and level of maturity.
We review your current needs matrix, data security controls, policy and procedure documentation, industry standards, and legal requirements. We aim to fully understand the present scenario, including the use cases, issues, and sensitive data flow. We study current data encryption capabilities and pinpoint areas in need of development. We provide an implementation plan to address the identified control gaps and design use cases to facilitate choosing and assessing potential encryption and other data protection solutions.
Although NIS 2 has several requirements, not all businesses and organizations must adhere to them. Different rules apply depending on the company’s operations and size. As a result, each relevant entity must follow a few fundamental rules.
1. Risk assessments and security policies for information systems
Our team has expertise in conducting comprehensive risk assessments that identify various forms of potential risks to your business operations. This assessment includes an analysis of the current security posture to identify vulnerabilities and threats, as well as the development of risk criteria to prioritize potential issues.
Major vulnerabilities identified, risk ratings for various assets, and a prioritized risk mitigation plan are all quantifiable deliverables of such assessments. These results enable firms to make better decisions on the resource allocation and strategies for risk management.
After risk assessment, we help organizations develop robust security policies that meet legal requirements and the best practices of the industry. The security policy framework involves data protection, incident response, access control, and compliance requirements. By enforcing such policies, organizations may set specific standards for protecting confidential data and handling security issues.
These policies are therefore, measurable, leading to improved regulatory compliance, shortening the incident response time, and raising general security awareness amongst personnel. This systematic way of working not only aids in enhancing the organization’s security posture but also brings forward a security-conscious culture at all levels.
2. A plan for handling security incidents
Our team can provide you with a clear incident response strategy, which is a critical necessity in the event of a security breach. This plan usually includes developing proper incident response processes, ways of communication, and escalation channels. The strategy also includes mechanisms for assessing incidents like ransomware attacks, phishing attacks, and data breaches after they occur in order to identify lessons learned and enhance future responses. By being ready for these situations, your company can react more skillfully and limit possible harm.
3. A plan for managing business operations during and after a security incident. This means that backups must be up to date. A plan must also be made to ensure access to IT systems and their operating functions during and after a security incident.
We can greatly improve your organization’s capacity to manage operations during and following a security event by offering experience, resources, and structured strategies. We can assist you in keeping your backups up to date by designing thorough backup plans and testing backups on a timely basis. Testing backups on a regular basis reduces downtime and interruption by ensuring that data can be restored precisely and promptly when necessary.
A strong continuity strategy must also be in place to ensure access to IT systems and their operational capabilities during and after a security event. We take an approach to confirm the dependability and integrity of your backups. We can assist you in establishing RBAC controls and IAM rules to guarantee that only authorized individuals have access to this private system data.
4. Security around supply chains and the relationship between the company and direct suppliers. Companies must choose security measures that fit the vulnerabilities of each direct supplier. Companies must then assess the overall security level of all suppliers.
Our team of professionals can assist your company in establishing supply chain security. We can assist you in understanding the vulnerabilities that your direct suppliers might expose you to and develop strategies to address such concerns. Risks associated with the supply chain include:
- Data breaches, which can result from unauthorized access to private information shared with suppliers.
- Quality control problems, which can cause product recalls or harm to your brand’s reputation.
- Regulatory compliance risks, which can expose your company to fines if suppliers violate industry standards.
After integrating the items from various vendors into the system, our professionals can assess your company’s overall security posture.
Tailored Encryption Services
We assess, strategize & implement encryption strategies and solutions.
5. Policies and procedures for evaluating the effectiveness of security measures.
Our specialists will be able to help your company develop and implement effective policies and procedures, as well as assess the efficiency of security measures. To maintain security and reduce the risk in an enterprise, there should be frequent reviews of the effectiveness of the security measures. Based on the size of the organization, complexity, and risk profile, we recommend quarterly or at least semiannual evaluations. We can make use of several assessment approaches, including the following in properly evaluating your security:
- Vulnerability assessments: Thorough reviews of your IT system to find and rank any weak points that hackers could exploit.
- Penetration Testing: A simulated cyber-attack by an ethical hacker is performed to find weaknesses that might be used before an attacker does.
We can also do a gap analysis of your existing rules against industry best practices and compliance standards and recommend solutions wherever required. A systematic review process can help your business verify that properly implemented policies and procedures help to reduce risks and adapt to the changing threat landscape.
6. Cybersecurity training and practice for basic computer hygiene
Our team also offers cybersecurity training, which is designed to provide the basic computer hygiene practices essential for safeguarding your organization. The training can be beneficial for teaching employees about securely accessing systems, changing unsafe password storage habits, and minimizing incidents of unauthorized use of software.
Our training focuses on the most pertinent threats to your organization, particularly phishing attacks and social engineering tactics. Most phishing attacks involve some kind of fraudulent email or message that can trick employees into giving away sensitive information by clicking on malicious links. Our training can help your employees develop the skills needed to detect such threats, identify the clear signs of phishing attempts, and respond correctly.
Similarly, social engineering techniques use human nature to deceive people into revealing confidential information. By training employees regarding these tactics, we can make them more aware and less susceptible to being manipulated, thus improving the security posture of your business as a whole.
Our training equips individuals with knowledge about various dangers and provides essential information for management to oversee the security practices of employees, services, or organizations. We can also offer a customizable checklist for regular maintenance, such as logging out of all accounts, shutting devices as needed, clearing your session and cookies, or any other measures that best suit your organizational needs. A cybersecurity-aware culture and basic hygiene practices within your organization will go a long way in reducing the risk of falling prey to phishing and social engineering attacks.
7. Security procedures for employees with access to sensitive or important data, including policies for data access. The company must also have an overview of all relevant assets and ensure that they are properly utilized and handled.
Our representatives can help your company develop detailed rules of data access that define who has access to sensitive information and when, ensure proper use and management of all sensitive information, and foster a culture of transparency. We can help you classify your data according to sensitivity levels to set the right access permissions. We advise the below categorization of various data types:
- Public Data: Public data is information that may be freely shared with the general public without danger. Examples include marketing materials and press releases.
- Internal Data: Information that should only be used internally and that might somewhat harm the company if shared. Examples include internal memos and employee handbooks.
- Confidential Data: This refers to the information that must be kept private, as disclosure could have severe damaging impacts. It includes customer information, financial data, and proprietary information.
- Restricted Data: This is sensitive information. If compromised, it can lead to serious consequences against the organization, including possible legal penalties and damage to its reputation. Examples include trade secrets and PII.
By classifying data in this way, the organization will be able to tell what controls and what security measures should be applied to each level. We can also assist in establishing an approval process to grant access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or handle it. We can also help organizations set up a proper approval process for accessing the data.
Besides that, periodically reviewing logs regarding data access is recommended. This practice helps monitor who accesses sensitive data, when, and for what purpose, allowing for the identification of any unauthorized access attempts or anomalies.
8. Policies and procedures for the use of cryptography and, when relevant, encryption.
Our team is prepared to help businesses identify the vital information that requires security. By doing this, we can assist businesses in creating efficient rules and processes for the use of cryptography and encryption. We take the time to understand each company’s unique needs, risks, and industry standards, allowing us to create customized policies that outline approved encryption methods, key management practices, and safe data transfer protocols.
Having a strong key management policy is vital for keeping encrypted data secure, and we’re committed to helping businesses achieve that. Proper key management involves the generation, distribution, storage, rotation, and destruction of encryption keys, which are vital for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. Without effective key management, even the strongest encryption can be rendered useless if keys are compromised or mishandled.
We can thoroughly review your existing policies and identify gaps or areas of improvement in cryptographic practices, ensuring that the policies cover all aspects of data security, from encryption to access control and monitoring. Cryptography and cybersecurity standards evolve quickly. To ensure the effectiveness of your encryption practices, it is crucial to adopt recognized encryption standards.
Some of the commonly used standards are RSA, an asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption—and AES, a symmetric encryption algorithm that is widely used across various applications, offers a high level of security, is advised for protecting classified information, and is widely adopted in commercial applications. It is commonly used for secure data transmission, digital signatures, and key exchange.
We can offer ongoing support to review and update policies as new threats, technologies, and regulations emerge, keeping businesses current and protected.
9. The use of multifactor authentication, continuous authentication solutions, voice, video, and text encryption, and encrypted internal emergency communication when appropriate
We can help your company select the best multifactor authentication techniques, including token-based, app-based, and biometric solutions. To provide additional protection, we can also help integrate these techniques into existing applications and systems. An enhanced security strategy that goes beyond conventional one-time verification techniques is continuous authentication.
Continuous authentication keeps an eye on and confirms a user’s identity throughout their entire engagement with a system instead of just doing so at the start of a session. This continuous assessment helps guarantee that the individual gaining access to private data or systems is still the authorized user.
We can help businesses select and deploy these solutions, which rely on behavioral biometrics, location tracking, and real-time risk assessments. Organizations can quickly identify and respond to potential security threats by continuously verifying user identity, minimizing the need for frequent re-authentication. We can also offer our expertise in selecting secure, compliant encryption solutions for voice calls, video conferences, and text messages. We can also set up encrypted emergency channels, ensuring rapid, secure communication during crises.
10. Security around the procurement of systems and the development and operation of systems. This means having policies for handling and reporting vulnerabilities.
Our team can assist in creating a structured Vulnerability Disclosure Policy (VDP) that outlines how vulnerabilities should be reported, assessed, and mitigated. This involves establishing the parameters of what is considered a vulnerability, creating transparent reporting procedures, and making sure that security researchers and ethical hackers are free to disclose findings without worrying about potential legal ramifications.
We assist companies in keeping a proactive approach to security by offering recommendations for assessing the seriousness of vulnerabilities and setting priorities for remedial efforts. Additionally, we can facilitate training and awareness programs covering best practices for identifying potential vulnerabilities during the procurement process and secure coding practices during development.
Secure coding practices include input validation, which ensures that all user inputs are validated and sanitized to prevent injection attacks; authentication and strict access control are implemented to protect sensitive data and resources; and sensitive information is avoided in error messages. In addition to secure coding practices, utilizing vulnerability scanning tools during development is crucial for identifying and mitigating security risks.
Some of these tools are Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Tools to source code for vulnerabilities without executing the program. Examples include SonarQube, Checkmarx, Fortify, and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) Tools, which test run applications for vulnerabilities by simulating attacks. Examples include OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, Acunetix, and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) Tools, which identify vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies. Examples include Snyk, Black Duck, and WhiteSource.
Conclusion
Enterprises need to upgrade their security procedures and, at the same time, be proactive in securing sensitive data. By establishing protocols for data access, identifying and fixing vulnerabilities, and reacting to any incidents, businesses may improve the security of their data. It can be beneficial to create these frameworks and include regulatory compliance while cultivating a security-conscious culture among staff members by collaborating with outside experts.
In addition, implementing technology, such as encryption for communications, multifactor authentication, and continuous authentication, can dramatically improve an organization’s chances of defeating a cyber-attack. Successful risk management requires cybersecurity training and a robust process for procurement and system development.
In the end, these procedures not only safeguard important data but also foster trust among clients and associates. As the threat environment evolves, enterprises must remain updated on cybersecurity trends to continuously meet the evolving regulatory standards to prosper in today’s digital world.
We can help you with your mission to adhere to this compliance. For assistance, please reach out to us at [email protected]