Securing your environment is very crucial in the current security-driven world. Every enterprise needs to secure their infrastructure against the rising threat. AppLocker is a security feature in Windows that allows your organizations or your enterprises to control which executable files or applications can run on your systems.
It prevents potentially harmful applications from being run by users by providing your administrators with the ability to create rules regarding the software that is allowed to be executed. This will also help in preventing unauthorized access to the applications and enhance the overall security of an organization.
Encryption Consulting’s CodeSign Secure is a code signing solution that is designed to manage digital code signing certificates and streamline code signing operations. Our solution, CodeSign Secure, simplifies the process of securely signing software and applications to ensure their authenticity and integrity. It provides an efficient way to handle code signing operations across diverse environments so that only verified software is trusted and deployed.
By integrating our solution with AppLocker, you can significantly enhance the security and control of your applications. While AppLocker can ensure that only whitelisted applications can run, our solution ensures that these applications are signed with trusted code signing certificates. This combination provides a strong mechanism to ensure that only validated and authenticated applications can be executed, which protects systems from malware or unauthorized applications.
What is Encryption Consulting’s Code Signing Tool – CodeSign Secure?
Our solution is designed to manage, automate, and secure code signing processes within your organization. It controls code signing certificates and ensures that only authorized users can sign software. Our solution reduces the risk of human error by automating signing processes, which also ensures that the distributed software is both secure and compliant with industry standards.
Key Features relevant to AppLocker:
-
Centralized Certificate Management
Our solution allows your organization to centrally store and manage all code signing certificates with secure access controls. System Admins can assign specific permissions to users or teams to ensure that only authorized personnel can sign applications. This feature aligns with AppLocker’s functionality, as it helps ensure that only software that is signed by trusted certificates can run.
-
Automated Code Signing Processes
Our platform automates code signing processes and reduces manual interactions to the minimum, making the processes less prone to errors or vulnerabilities. Automated workflows ensure that the code is always signed correctly before being distributed, which provides seamless integration with AppLocker and ensures that your organization will distribute only validated and signed applications.
-
Compliance Monitoring and Reporting
Our platform includes built-in compliance features that track and report all code signing activities your organization performs. Detailed audit logs will help your organization meet regulatory requirements and internal policies. When used with AppLocker, this ensures that your organization only runs software that meets security and compliance standards.
-
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Our solution integrates with existing CI/CD Pipelines and automates the signing process during software development and deployment. This streamlines code signing in agile environments while maintaining high security. With AppLocker, it guarantees that all of your organization’s software running in production is signed, trusted, and verified without disturbing the development workflow.
Why Use CodeSign Secure with AppLocker?
-
Enhanced Security
Our solution, CodeSign Secure, offers centralized management of your organization’s code signing certificates and ensures only authorized personnel can access these certificates for signing. By securely storing and managing these certificates, we help your organization reduce the risk of misuse or accidental exposure. When paired with AppLocker, this creates an extra layer of security, as only signed software from your organization is allowed to run by enforcing necessary policies.
-
Streamlined Code Signing
Our solution automates the code signing process and minimizes the potential of human error to ensure consistent signing practices. This automation ensures that your developers and system administrators don’t have to manually handle the code signing certificates, which reduces delays and risks associated with manual processes. When integrated with AppLocker, this streamlined process guarantees that only signed and trusted applications are executed by your organization.
-
Improved Compliance
Our solution provides detailed reporting and monitoring features that track all code signing activities. These reports offer detailed insights to your auditors into which application or software was signed, by whom, and when. This will also help your organization meet regulatory compliance requirements like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or CAB Forum. By integrating this feature with AppLocker, your organization can not only prevent untrusted applications from running but also ensure that all running software meets internal and external compliance standards.
How does AppLocker use Code Signing for Application Control?
AppLocker uses code signing as a critical method for verifying the identity of software publishers and enforcing strict control over which applications can run on your organization’s systems. By leveraging digital signatures, AppLocker ensures that only trusted and signed software can be executed.
AppLocker Rule Types
AppLocker operates through different rule types to control various file formats and application types. Let’s take a look at these rule types:
-
Executable Rules
These rules control which executable files (.exe and .com) are allowed to run in your organization. Administrators can create rules based on the file’s publisher, path, or file hash to ensure that only trusted executable programs are run.
-
Windows Installer Rules
These rules manage which Windows Installer files (.msi and .msp) can be executed. This allows your organization to control the installation of software packages and limit these installations to trusted sources.
-
Script Rules
These rules govern the execution of script files such as PowerShell Scripts (.ps1), batch files (.bat), and JavaScript files (.js). This is essential in controlling the execution of potentially harmful scripts within your organization’s environment.
-
Packaged App Rules
These rules apply to Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps and packaged apps like AppX files. They control the execution of modern applications distributed via the Microsoft Store or other channels, ensuring only authorized applications can run.
Publisher Rules and Digital Certificates
AppLocker can use these rules to enforce application control based on digital signatures. When the software is signed using a code signing certificate, the digital signature is embedded in the file, which allows AppLocker to identify the publisher and ensure that the application is authentic and hasn’t been tampered with.
-
How Publisher Rules Work
These rules are based on the metadata from a file’s digital certificate, such as the publisher and product’s name, file version, and certificate issuer. When an administrator from your organization creates a rule, they can specify different levels of control.
-
Using Code Signing Certificates
AppLocker uses the digital signature to verify the identity of the software publisher before allowing the application to be run in your organization’s environment. This process works as follows:
- The application is signed with a code signing certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to your organization.
- AppLocker then checks this certificate to confirm that it was issued by a trusted CA and whether it matches the application or not.
- If the certificate is valid and meets the defined publisher rule, the application can run.
Implementing Code Signing using CodeSign Secure for AppLocker
Now, let’s discuss how you and your organization can use CodeSign Secure along with AppLocker to secure your development and deployment workflows.
Setup CodeSign Secure
- Visit our website and sign up for a CodeSign Secure account if you haven’t already done so.
- Complete the registration process and gain access to our solution.
- Log in to the portal (based on the deployment you chose – On-Prem, SaaS, or Hybrid).
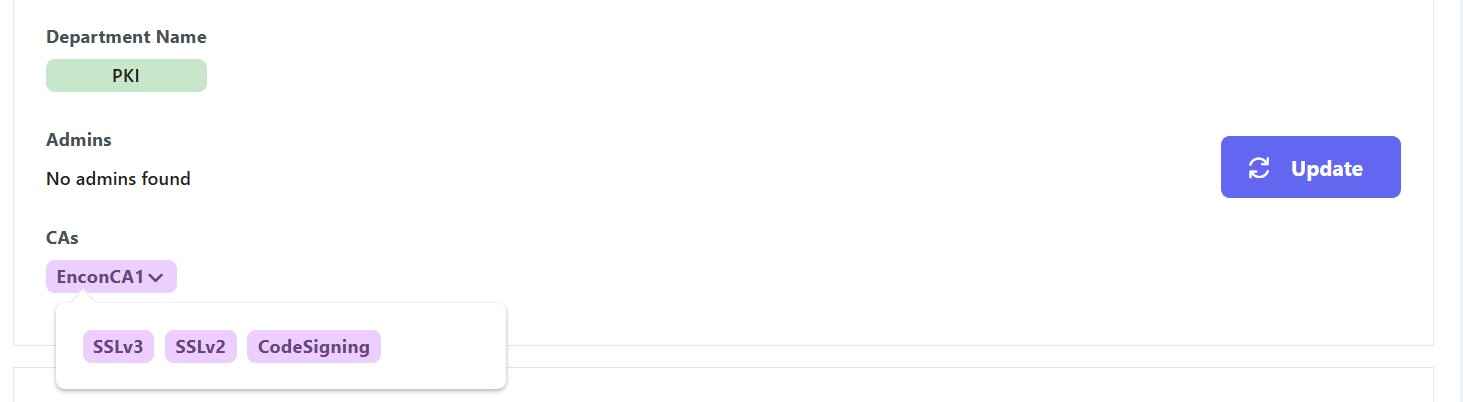
- Define user roles such as System Admin, Project Manager, Security Officer, Auditor, and Developer on our portal.
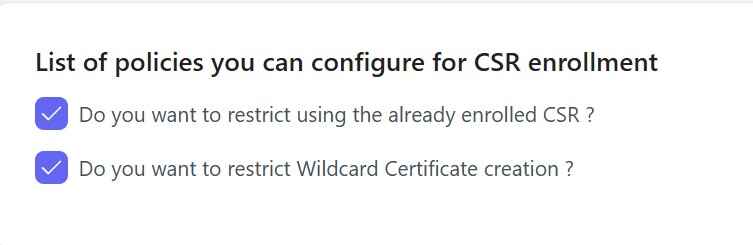
- Set up access controls and permissions so that only authorized personnel can perform the code signing operations.
- Integrate our solution with your existing CI/CD pipelines like Jenkins, GitLab, Azure DevOps, and so on to automate the code signing processes during the build and deployment stages.
Obtain Code Signing Certificates
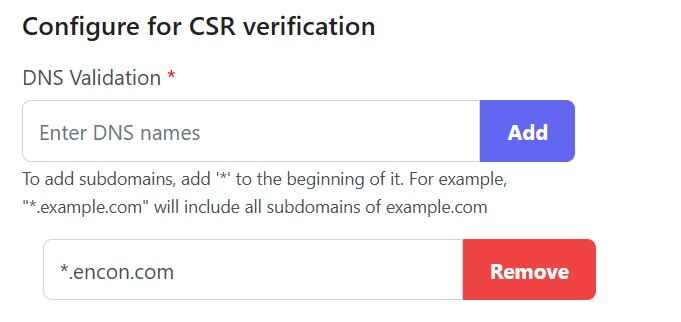
- Use our portal to generate a CSR by storing the private cryptographic key in a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 HSM for security.
- Use that CSR to obtain a code signing certificate from a trusted public CA.
- Choose the type of certificate based on your security needs:
- OV (Organization Validation): Standard level of validation for organizations.
- EV (Extended Validation): Offers the highest level of validation for enhanced security.
- Once you receive the issued certificate, store it in our portal by importing the certificate.
- Now, ensure that this certificate is only accessible to those with proper roles and permissions.
Code Signing Process
- Use our KSP (Encryption Consulting’s Key Storage Provider) to sign executables, scripts, or other files with the issued certificate.
- Automate this code signing process through your CI/CD pipeline or use our custom-modified Utility Tool to sign individual or bulk files.
- Once the software or application is signed, Windows should recognize the digital signature as coming from a trusted publisher.
- Test the signed files on your Windows systems to verify the signature and ensure that the applications meet security policies.
Configure AppLocker to Use Publisher Rules
- For single machines, you have to use secpol.msc (Local Security Policy) to access AppLocker settings. But for domain-wide policies, you have to use gpmc.msc (Group Policy Management Console) to manage AppLocker policies.
- You have to go to Application Control Policies > AppLocker, and you have to select the rule type like – Executable Rules.
- Now, you need to select Create New Rule and choose Publisher as the condition.
- After that, browse to a previously signed executable file to extract the publisher information from the certificate you used for singing.
- Now, the administrators in your organization have to define the scope of the rule, such as what versions of the product are to be released.
- Then, you have to apply these rules to relevant user groups.
- Remember to configure your AppLocker in audit mode to monitor the logs.
Deploy and Enforce AppLocker Rules
- After you have verified the rules in Audit mode, switch your AppLocker to Enforce Mode. In this mode, only the trusted certificate will be allowed to execute to maintain your organization’s security.
- You should regularly review the AppLocker Logs to detect any attempts to run unauthorized software.
Best Practices for Using CodeSign Secure with AppLocker
Follow these few best practices to keep your organization secure and authenticate applications using our solution – CodeSign Secure integrated with AppLocker. These are:
-
Regularly Update Certificates
You should ensure that your code signing certificates are renewed before they expire to avoid any kind of interruptions in software trust and prevent the execution of unsigned or untrusted code. You should set up automated alerts for certificate renewal and plan for a smooth transition between old and new certificates.
-
Monitor AppLocker Logs
Your developers should regularly review AppLocker logs using Event Viewer to monitor application execution and detect potential security incidents. These logs will also help you track rule violations or policy misconfigurations, ensuring that only trusted software is executed across your organization’s environment.
-
Automate When Possible
Your developers should leverage automation tools to integrate our CodeSign Secure with CI/CD pipelines and deployment processes. This ensures that code signing is consistently applied during software builds and releases and reduces the chances of manual errors.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Let’s discuss a few of the common issues we can face during the use of AppLocker. These are as follows:
-
Certificate Recognition Issue
-
AppLocker Doesn’t recognize CodeSign Secure issued certificates:
-
Missing Intermediate Certificates: If AppLocker fails to recognize our CodeSign Secure issued self-signed certificates, this may be due to missing intermediate certificates in the certificate chain. To resolve this, you need to follow these steps:
- You must download and install the missing intermediate certificates from our CodeSign Secure portal.
- You must check whether the certificate chain is present in the Windows Certificate Store or not and whether they are properly linked.
-
Expired Certificates: If the certificates have expired, AppLocker will block the associated software from your organization. To fix this:
- You must renew the certificate before it expires.
- You need to re-sign the affected software using the new certificate and update AppLocker rules as necessary to reflect this new certificate’s information.
- Certificate Store Configuration: Your developers need to make sure that the certificate is installed in the correct store for code signing.
-
Missing Intermediate Certificates: If AppLocker fails to recognize our CodeSign Secure issued self-signed certificates, this may be due to missing intermediate certificates in the certificate chain. To resolve this, you need to follow these steps:
-
AppLocker Doesn’t recognize CodeSign Secure issued certificates:
-
Certificate revocation Issue
-
Problems Accessing Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or OCSP:
-
Network Restrictions: Your system’s firewalls or network settings may block access to CRL distribution points or OCSP responders, which will prevent AppLocker from verifying the certificate’s revocation status. To solve this problem, you need to follow these resolutions:
- You must verify that your firewall and network allow outbound traffic to the URLs specified in the CRL Distribution Points or OCSP locations.
- If your automatic CRL updates fail, you need to manually download the latest CRLs from the CA’s website and install them.
- If your organization prefers isolated and high-security environments, then you need to set up internal CRL Distribution points or OCSP responders.
-
Network Restrictions: Your system’s firewalls or network settings may block access to CRL distribution points or OCSP responders, which will prevent AppLocker from verifying the certificate’s revocation status. To solve this problem, you need to follow these resolutions:
-
Problems Accessing Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or OCSP:
-
Error Codes and Resolution
-
Invalid OID (Object Identifier): This error occurs when the code signing certificate’s OID doesn’t match the expected OID for the required application. To resolve this issue, you need to follow these steps:
- You need to check the certificate’s Enhanced Key Usage (EKU) settings to confirm that it has the correct OID for code signing.
- Your developers must ensure that the certificate is specifically issued for code signing purposes.
-
Signature Validation Failures: Windows or AppLocker may fail to recognize the digital signature for several reasons:
- You need to ensure that the software hasn’t been tampered with since signing, as any changes would invalidate the signature.
- You must verify the certificate’s revocation status by ensuring that your system has access to CRLs or OCSP.
- You need to confirm that the correct signing procedure was followed, along with the appropriate certificate and process.
-
Common Error Codes:
- HRESULT: 0x800710D8: This error signifies an issue with your certificate chain or the end-entity certificate is untrusted. You must verify the certificate chain and reinstall the root or intermediate certificates if necessary.
- 0x8009000F (Key not valid for use in a specific state): You need to check whether the private key associated with the certificate is accessible and correctly configured or not. You must reimport the certificate if required.
- 0x800B0109 (The certificate chain was issued by an authority that is not trusted): You need to install the root and intermediate certificates from the certificate authority and confirm the certificate trust settings.
-
Invalid OID (Object Identifier): This error occurs when the code signing certificate’s OID doesn’t match the expected OID for the required application. To resolve this issue, you need to follow these steps:
Conclusion
Using CodeSign Secure with AppLocker offers several significant advantages, such as enhanced security, compliance, and streamlined management. We encourage you to explore the benefits of integrating our solution with AppLocker to secure your applications and IT infrastructure. By adopting this solution, you can enhance your application control, reduce security risks, and ensure only trusted software runs within your environment.
To start securing your software today and take advantage of our solution’s robust code signing features, visit our website to learn more about CodeSign Secure. Discover how you can integrate this solution with AppLocker to achieve a higher level of security and compliance in your organization.