Today, most organizations utilize Hardware Security Modules, or HSMs, within their security infrastructure. Whether it be for compliance standards, general security, or any other reason, most companies will have one or several HSMs for securing encryption keys. Configuring an HSM can be a complicated task, but the truly difficult part of using HSMs is the management of those devices.
Managing an HSM includes ensuring your HSM meets the policies of your organization, that it is compliant with any standards that your industry may abide by, and that only those who should be able to access and create encryption keys can create and access those keys.
Understanding HSMaaS
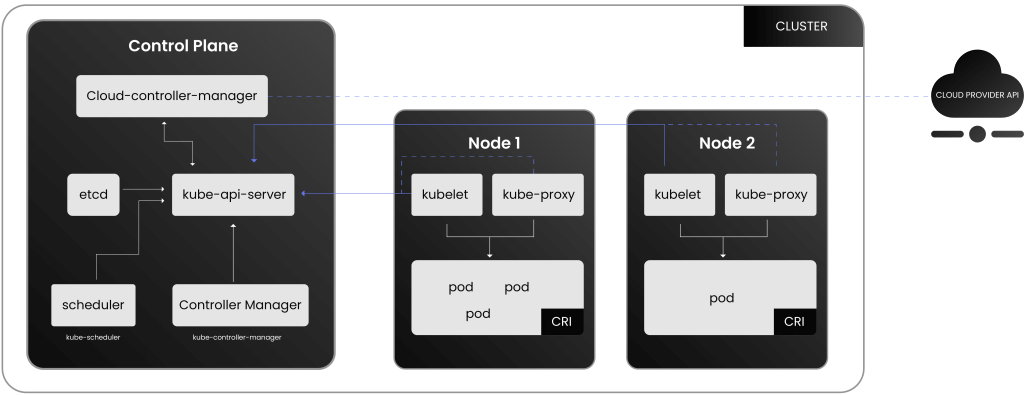
HSM-as-a-Service or HSMaaS, is different than just having an HSM in your organization itself. With an HSM in your organization, you normally oversee every aspect of it. Monitoring, configuration, and updating the HSM would all fall into your company’s hands. Though you would have complete control over your keys, managing everything gets complicated. Configuration of an HSM is a long process that can lead to many different issues along the way.
During configuration, you will likely need multiple team members as there are several different roles within the HSM, and it is recommended that you have each role be a different team member. Additionally, when dealing with quorums of those roles, you will need even more team members. When monitoring and upgrading HSMs, your organization will need to continuously monitor the HSM, taking up time and employee manpower, and you will need to stay up to date on the latest releases of software and firmware of the HSM.
When utilizing an HSMaaS, all the steps of the process are made infinitely easier. Configuration of the HSM is done by the organization offering the HSMaaS. The HSMaaS provider will take care of any daily monitoring of the HSM as well, clearing up manpower from your organization. Usually, if there are specific policies or standards your HSM needs to adhere to, they will also ensure your partition and the HSM meet those standards and policies.
Additionally, any firmware and software updates will be taken care of by the HSMaaS provider. One important point to note about HSMaaS is that the HSMs tend to be shared by other organizations working with the HSMaaS provider. What this means is that your keys will not be the only keys on the HSM. Luckily, HSMaaS providers have already found a secure method of doing this.
Although your keys are on the same HSM as other companies, you cannot access their keys, and they cannot access yours. They are split into different sections of the HSM that are inaccessible to anyone other than those allowed access to it. In this way, you have access and control over your keys, and no one outside of your organization can access them.
Benefits of HSMaaS for an Enterprise
There are several different benefits associated with HSMaaS. We have touched on a few of these benefits, but let’s dig a little deeper into why HSMaaS provides so many benefits to organizations:
1. Manpower Usage
When dealing with an HSM at your data center or on-premises, you will oversee every aspect of the HSM. That includes monitoring, access to the HSM and keys within the HSM, upgrading the firmware and software, and adding any new users, partitions, etc. With HSMaaS, you do not need to invest any manpower into the HSM. This will clear up your team members so they can focus on other tasks without needing to spend time managing the HSMs. You can instead trust your HSMaaS provider to take care of this for you.
2. Cost and Time Management
The cost associated with HSMs tends to be the price tag for most organizations, but another cost you should consider is the time cost. With an HSMaaS provider, all the time that a team or team member would spend on monitoring and maintaining an HSM will now be focused on other things, like client work. The actual cost of an HSM should also be considered when deciding to use HSMaaS.
HSMs can carry a high cost, as not only does an organization need to pay for the HSM itself, but they will also need to pay for the data center space and, if they are setting up the HSM in the most secure way possible, they should also purchase a backup HSM. With HSMaaS, the cost of the HSM is reduced to the service price. Usually, this will be significantly cheaper than buying and maintaining one yourself, as you will just be paying for a section of space on an already-in-place HSM.
3. Security
Security is a key component of utilizing an HSM. By allowing an HSMaaS provider to take control of your HSM, you never need to worry that it is secure. HSMs, in general, are tamper-evident and tamper-proof, but since the HSMaaS provider is protecting customer data, they will take even more steps to ensure the security of the HSM.
Control over who can access the HSM is strictly controlled so that only members of your organization who should have access to the HSM have that access. Additionally, the HSM will always be stored in a data center requiring IDs of the HSMaaS provider to ensure no one can physically get to the HSM.
4. Scalability and Versatility
When you run out of space in a partition, for example, and you need to expand your HSM use, this is even simpler with an HSMaaS provider. If your company was running the HSM, it could take a decent amount of time to create a new partition and get it set up with a client. In the HSMaaS case, it is as simple as reaching out to the provider, who will then take care of provisioning what is necessary on the HSM.
5. Compliance
Finally, there is the idea of compliance. With your own HSM, you oversee ensuring that your HSM meets all your compliance needs. This can take up a lot of time and manpower from your teams. In the case of HSMaaS, they are trained professionals who will work with you to ensure your HSM meets all your compliance needs.
Customizable HSM Solutions
Get high-assurance HSM solutions and services to secure your cryptographic keys.
Key Components of HSMaaS
The key components of HSMaaS are very straightforward. The HSMaaS provider gives you the ability to trust that your private keys are always secure, taking the stress out of managing and protecting your HSM yourself. Also, HSMaaS frees up your employees to focus on other tasks, taking away the need to continually monitor the HSM and ensure that it is staying compliant and up to date. Finally, with HSMaaS, you do not need to take the time to create new partitions, users, etc., as the HSMaaS provider takes care of this for you, along with ensuring that your keys are secure throughout their lifetime.
Implementing HSMaaS in Your Organization
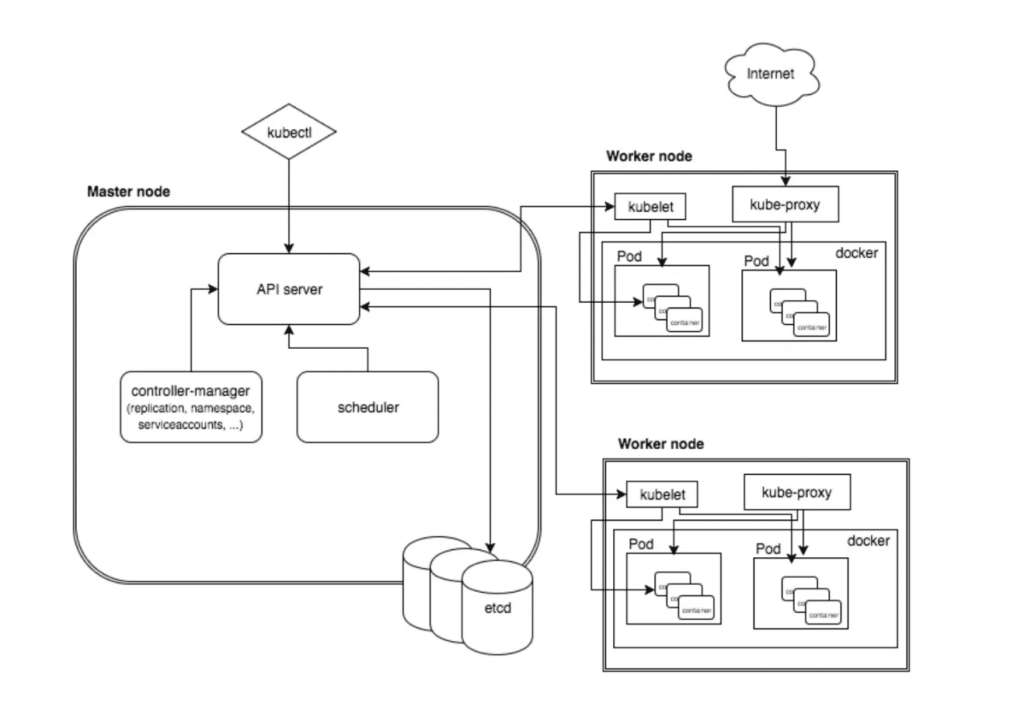
Implementing an HSMaaS in your organization is an extremely simple matter. Originally, with your own HSM, you would need to take care of several steps yourself. First, you would need to purchase the HSM and initialize it. The configuration of an HSM can take a day or more, depending on your familiarity with HSMs. As most organizations are using an HSM for the first time, it can take three days to deal with configuration issues and networking problems. After initializing the HSM, you must set up the policies to meet the compliance requirements of your industry.
This can include setting up user roles and setting policies on the HSM. After this, you must create your first test keys to ensure that the HSM is functioning properly. If any part of this process is not working, it is up to you to contact the manufacturer and get a replacement HSM. As part of the key creation process, you must also set up your client machine as a client of the HSM. Finally, you must integrate your HSM with all the systems that need it. This can include your PKI, your code-signing services, and any other tools that may create key pairs or certificates.
In the case of HSMaaS, it is a much simpler process. Instead of needing all the beginning steps, you can skip right to making your machine a client of the HSM and integrating it with your systems. The HSMaaS provider will already have the HSM configured; they may just need to set up the policies to meet specific compliance standards.
Setting yourself up as a client is a very simple process, and at Encryption Consulting, we can help you with every step of your integration journey. If you utilize our HSMaaS offering or wish to set up your own HSM and need assistance, we are here to help. Our team of experts has worked with most HSM integrations, and we can make it a simple and painless process.
Case Studies and Success Stories
At Encryption Consulting, we have provided HSMs as a Service to a number of different clients. These clients have all utilized different deployment options and HSM types and have been in different industries. We had a healthcare organization come to us for assistance with their PKI and the HSM they should use. This company was moving its PKI to the cloud, so our expertise was needed to begin that process.
We set up their entire PKI and provided them with multiple guides on how to maintain the PKI, monitor the PKI, and complete day-to-day operations. Along with the PKI came their desire to integrate an HSM within their PKI. At first, they wanted to buy their own, but they found that the cost and manpower benefits of utilizing an HSMaaS made more sense.
Their biggest stress was that the keys in our HSM would be accessible to other users of our HSMaaS. Still, we explained the architecture of the HSM type in use, and they understood that only those people from their organization who should be able to access the keys would be able to access them.
Another success story we have had is an integration with our code-signing product, CodeSign Secure. We had a client who was utilizing our on-premises HSMaaS within their PKI, and they wanted to start using a code-signing product at their organization. After reviewing a number of different code-signing products, the organization found that CodeSign Secure had the most appealing features and cost. They wanted to set up their CodeSign Secure client and server on the cloud while they utilized an on-premises HSMaaS.
The integration went extremely smoothly, and they did not need to worry about any extra steps like configuring a new HSM or managing the different components of the HSM. They could seamlessly integrate their HSMaaS with CodeSign Secure while still utilizing it to its full capacity with their PKI. As you can see, using an HSMaaS offers many different benefits to organizations, allowing these companies to rest assured that their data is secure and properly monitored at all times without the need to utilize their team members in this process.
Best Practices for Managing an HSMaaS
While the majority of the work of managing an HSM is taken out by using an HSMaaS, it is still important to take certain steps to ensure the HSMaaS is running and being managed to your organization’s standards. Some of the best practices your organization should follow can be seen below:
Ensure the HSMaaS Provider is keeping the HSM up to your organization’s policies:
When selecting an HSMaaS Provider, you should ensure that they meet all your organization’s policies in regards to monitoring and protecting data. Making sure the HSM is in FIPS mode, if necessary, and that the data is accessible to only your organization are two key questions you should ask the HSMaaS provider. Additionally, ensure that the HSMaaS provider is monitoring the HSM with enough regularity so that your company’s policies are met.
Alert the HSMaaS Provider to any policy changes or standard changes:
If your organization goes through any large or small policy changes that relate to the HSM, it is very important to update your HSMaaS provider on this fact. This will keep the HSM up to date on organizational policies and ensure that it still functions with the proper security in place.
Ensure you are getting updates on the status of the HSM regularly:
Another best practice is to ensure the HSMaaS provider is giving regular updates on changes, upgrades, and the status of the HSM. This can be a weekly or monthly meeting, and it is even better if they have a webpage continually showing the status and updates of the HSM.
Future Trends in HSMaaS
We at Encryption Consulting have noticed a large trend in HSMs in general and HSMaaS providers for the future. Many HSMaaS providers offer different deployment options for users, meaning you can have an on-premises or cloud-based HSM. This trend is because so many organizations are moving toward the cloud for most of their services. Another future trend you will find a lot more often in all cybersecurity is the idea of Post Quantum Cryptography or PQC. PQC is the idea of preparing systems and algorithms for the threat that quantum computers will pose in the near future.
Most of this PQC-readiness involves changing out old algorithms, like RSA, with algorithms that are considered quantum-safe. This is because classical computers would take several decades to decrypt a single password encrypted with RSA, whereas, with a quantum computer, this would take seconds. As you can see, preparing your systems for the future is extremely vital, which is why we highly recommend HSMaaS.
Becoming PQC-ready is a long and arduous process that can take years. By using HSMaaS and ensuring they are in the process of becoming PQC ready, you can save a lot of time and effort in getting your HSM PQC ready.
Customizable HSM Solutions
Get high-assurance HSM solutions and services to secure your cryptographic keys.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
We have talked about a number of different things in regard to HSMs as a Service, but one more important point is questions we, as HSMaaS providers and consultants, are asked by customers. One of the first and most important questions we are asked is how do I determine if an HSMaaS is a good fit for our organization? Since HSMs as a Service can be used in both the Cloud and on-premises, an HSMaaS should work for any organization.
It cuts down on the cost of money and manpower, and it provides everything an organization would need from an HSM. The only time an HSMaaS would not be able to be used by a company is if they have specific policies or standards that restrict the use of an HSMaaS provider. In this case, the HSM would have to be managed by your organization. Another common question we are asked is whether HSMs as a Service are as secure as an organization-owned and controlled HSM.
Yes, an HSMaaS functions in exactly the same way that an organization’s own HSM does and tends to be a bit more secure. The reason for this is that the HSMaaS provider’s sole focus is on the HSM, so all updates are done on time, any issues with the HSM are handled by trained professionals, and they know the best practices involved with securely running and monitoring an HSM.
One final frequently asked question we are posed is: what is the best way to get started with using an HSMaaS? Our best suggestion is to speak to multiple HSMaaS providers and compare their prices and offerings. Many will charge more but offer less, but at Encryption Consulting, we are competitively priced and provide you with everything you need regarding your HSMaaS.
How Encryption Consulting Can Help
At Encryption Consulting, we offer several different services to customers, including our HSM as a Service offering. With our HSMaaS, you can utilize any type of deployment option you deem necessary. Utilizing an on-premises or cloud-based HSM is very simple with our HSMaaS model. With on-premises HSMs, you get the high-performance and low latency necessary for your applications; you have complete and isolated control of your keys, and if your organization requires strict data protection in specific countries, then the on-premises HSM is perfect.
Small and medium organizations may utilize cloud-based HSMs for multi-cloud platforms, highly variable workloads, and integration with cloud-based services. Additionally, we offer the option for the HSM to be dedicated or managed. Our dedicated HSMs are ideal for organizations that need a new HSM infrastructure and require designing and deploying.
As for our managed HSM option, this is ideal for organizations with the HSM infrastructure but who require assistance with management. Encryption Consulting will handle HSM provisioning, configuration, patching, and maintenance. We also offer design, implementation, and management of HSM systems if you require these services.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are a number of different points to consider when looking at an HSMaaS. Comparing service providers, understanding how an HSMaaS works, and knowing the best practices to employ when using an HSMaaS are all vital steps in selecting an HSMaaS for your organization. Additionally, understanding what using an HSMaaS vs an HSM is like is very important as well.
Our enterprise guide to HSMs as a Service should have prepared you with any questions you need to ask an HSMaaS provider and explained everything you need to understand an HSMaaS better. If you have any further questions, please contact us for more information on HSMaaS and how we can help you in your HSMaaS journey.